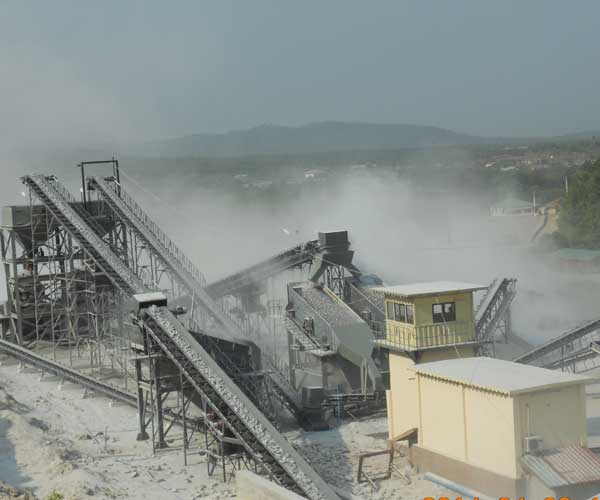
Quarry crusher machines are essential equipment in the mining and construction industry, responsible for breaking down large rocks into smaller, more manageable sizes. These powerful machines are designed to handle a wide range of materials, from soft sandstone to hard granite.
24 Online Service

A quarry is a type of open-pit mine from which rock, minerals, or other materials are extracted. Quarries are typically used for the excavation of stone, sand, gravel, and other construction materials. The extracted materials are then processed, crushed, and screened to produce various aggregate sizes for use in construction projects, such as road building, concrete production, and landscaping. Quarrying plays a significant role in providing essential raw materials for modern infrastructure and construction.
Quarry operations involve extracting, processing, and transporting materials such as stone, sand, and gravel. Crusher machines play a critical role in the initial stages of processing by breaking down large rocks into smaller, more manageable pieces. This not only ensures efficient transport and use of the materials but also enables the production of different aggregate sizes, which are vital for various construction applications.
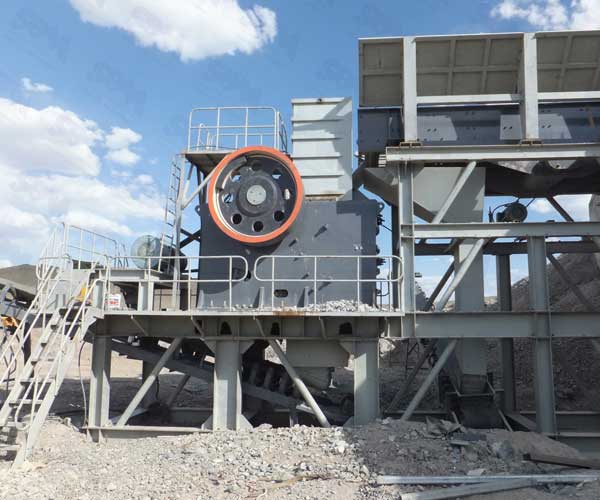

Jaw crushers are one of the most common types of crushers found in quarries. They consist of two plates or jaws – one fixed and one that moves back and forth. As the movable jaw compresses the material against the fixed jaw, it breaks into smaller pieces. Jaw crushers are ideal for primary crushing and can handle a variety of materials, including hard and abrasive rocks.
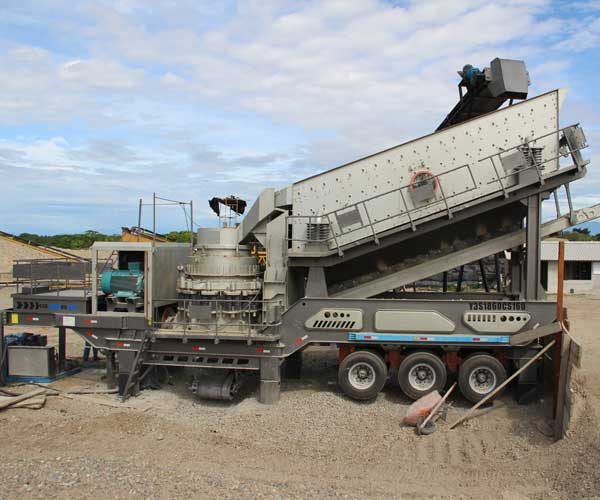

Cone crushers are designed for secondary and tertiary crushing stages. They use a rotating cone that crushes the material against the surrounding walls. Cone crushers are best suited for medium to hard materials and produce a uniform product size. They are commonly used for producing aggregates for road construction and railway ballast.
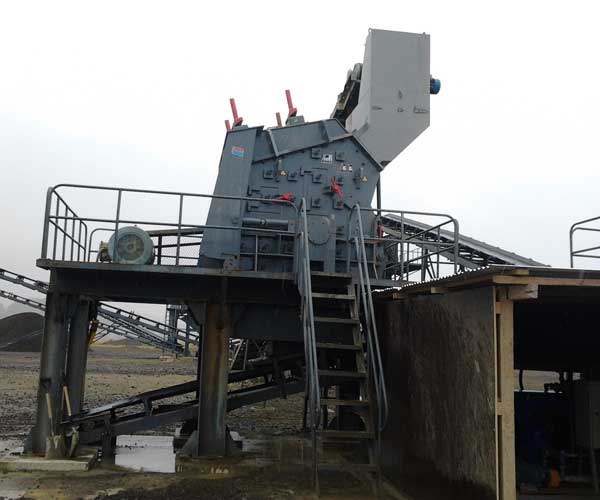

Impact crushers use the force of impact to break down materials. They feature a rotor that spins at high speed, hurling the material against a series of impact plates or hammers. This action results in the material being broken into smaller pieces. Impact crushers are ideal for processing soft to medium-hard materials, such as limestone or sandstone, and can produce a more cubical product shape.
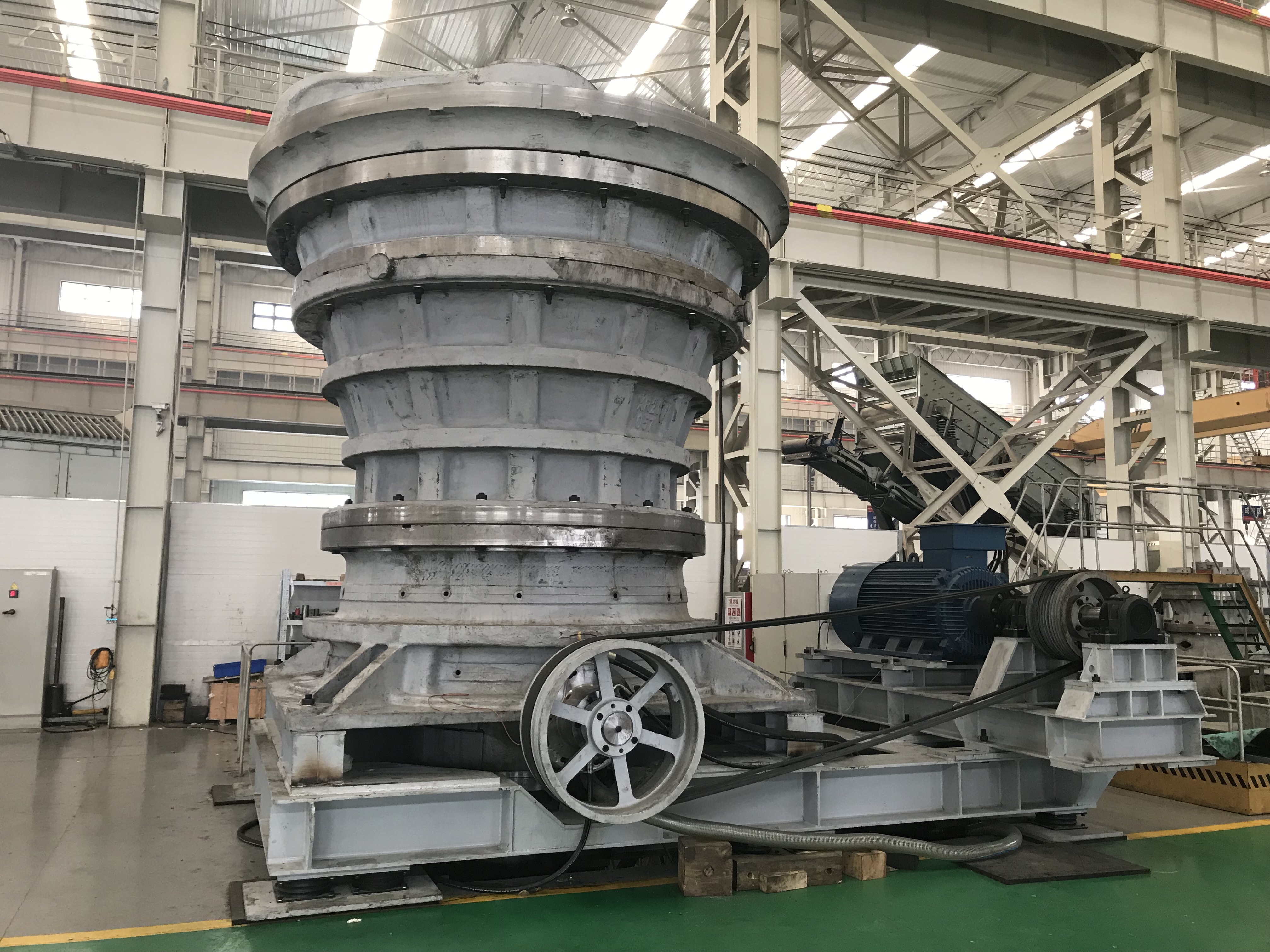

Gyratory crushers operate similarly to cone crushers, but with a larger crushing chamber and a central axis that rotates, crushing the material against the chamber walls. They are typically used for primary or secondary crushing and can process hard and abrasive materials. Gyratory crushers are often used in large-scale mining operations due to their high capacity.
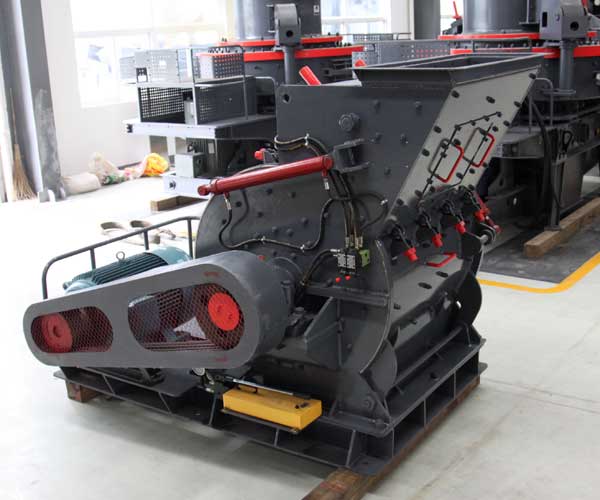

Roll crushers consist of two cylindrical rolls that rotate in opposite directions, compressing the material between them. They are suitable for medium to soft materials and can produce a relatively uniform product size. Roll crushers are often used for coal processing and can also be used for crushing materials like clay or shale in brick manufacturing.
Rock crushing is an integral part of the quarrying process, responsible for transforming large rocks into smaller, more manageable sizes suitable for various construction applications. The process typically involves multiple stages, each designed to handle specific tasks and produce different aggregate sizes.
The rock crushing process in a quarry can be broadly divided into four stages:
Primary Crushing: The first stage reduces large rocks into smaller pieces, typically 6 to 10 inches in size.
Secondary Crushing: This stage further reduces the size of the material, typically to a range of 1 to 3 inches.
Tertiary Crushing: In some cases, an additional stage is required to produce even smaller particles, often less than 1 inch in size.
Screening and Washing: The final step involves separating the crushed material into different size categories and washing it to remove impurities.
Primary crushing is the first stage of the rock crushing process and usually involves a jaw or gyratory crusher. These crushers use compression to break the rock into smaller pieces, suitable for further processing.
Jaw Crushers: Jaw crushers consist of two plates or jaws, one fixed and one that moves back and forth. The material is fed into the crusher, and as the movable jaw compresses the material against the fixed jaw, it breaks into smaller pieces. Jaw crushers are ideal for primary crushing and can handle a wide range of materials, including hard and abrasive rocks.
Gyratory Crushers: Gyratory crushers are similar in principle to jaw crushers, but with a larger crushing chamber and a central axis that rotates. The material is crushed between the rotating crushing head and the chamber walls. Gyratory crushers are suitable for primary or secondary crushing and can process hard and abrasive materials. They are often used in large-scale mining operations due to their high capacity.
Secondary crushing is the next stage in the rock crushing process and typically involves a cone or impact crusher.
Impact Crushers: Impact crushers use the force of impact to break down materials. They feature a rotor that spins at high speed, hurling the material against a series of impact plates or hammers. This action results in the material being broken into smaller pieces. Impact crushers are ideal for processing soft to medium-hard materials, such as limestone or sandstone, and can produce a more cubical product shape.
In some cases, a tertiary crushing stage is necessary to produce even smaller particles for specific applications. This stage may involve a vertical shaft impact (VSI) crusher or a high-pressure grinding roll (HPGR) crusher.
VSI Crushers: VSI crushers use a high-speed rotor and wear-resistant tips to break the material by impact. The crushed material then exits the crusher through a series of screens, producing sand-like particles. VSI crushers are used for producing fine aggregates and manufactured sand.
HPGR Crushers: HPGR crushers use two counter-rotating rolls to compress the material between them. This results in the formation of microcracks in the rock, which makes it easier to break down into smaller particles.
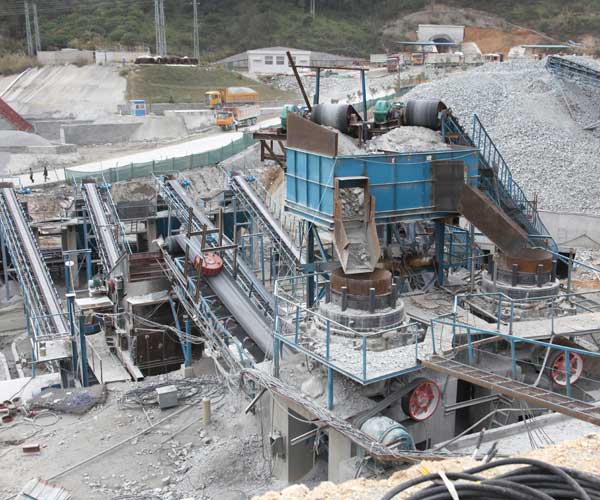

Quarries are vital sources of materials like stone, sand, and gravel, which are essential for construction, infrastructure, and landscaping projects. The quarry crushing process involves breaking down large rocks into smaller, more manageable sizes that can be used in various applications
The extraction process begins with identifying a suitable site for quarrying. Geologists and engineers evaluate the geological characteristics and mineral composition of the area to ensure the quarry will yield a sufficient quantity and quality of material. Once a site is chosen, the following steps are involved in the extraction process:
Once the extracted material arrives at the crushing area, it undergoes several stages of crushing and screening to produce the desired aggregate sizes. These stages include:
After the crushing and screening process, the material is classified into different aggregate categories based on size and shape. These categories include:
Once the aggregates are produced, they are stored in stockpiles according to size and type.
Choosing the right crusher for a specific quarry operation depends on several factors:
Our Projects
Copyright © ZENITH, All Right Reserved.