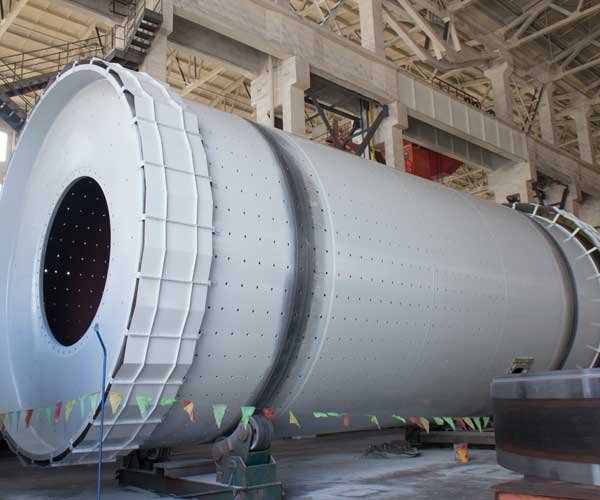
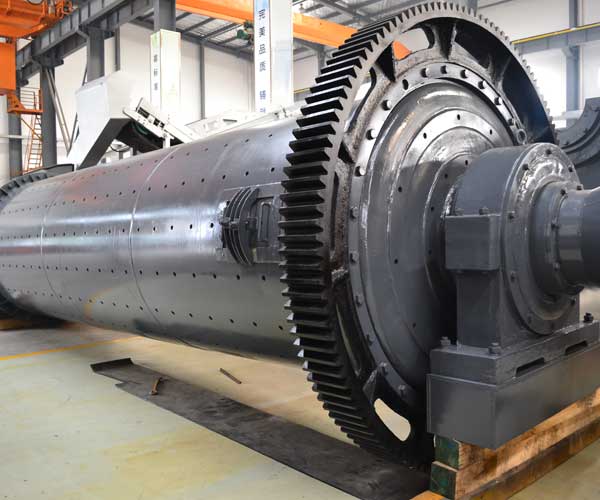
Ball Mill Maintenance and Repair Method
Ball mills are essential equipment in various industries such as mining, cement, metallurgy, and more. These cylindrical devices are used to grind and blend materials, transforming them into fine powders. To ensure optimal performance and extended equipment lifespan, regular maintenance and timely repairs are crucial.
Regular Inspections and Maintenance
Regular inspections are crucial to identify any potential issues and address them before they escalate into major problems. Scheduled inspections should encompass various components, including the mill shell, liners, mill bearings, lubrication systems, and drive systems. By detecting early signs of wear, misalignment, or component failure, maintenance teams can take proactive measures to rectify the problems promptly.
Lubrication System Maintenance
Proper lubrication is essential for the smooth operation of ball mills. Lubrication systems must be maintained regularly to ensure an adequate supply of lubricant and prevent equipment failure. Here are some key aspects to consider:
- Lubricant Selection: Choose the appropriate lubricant based on the mill’s specifications and operating conditions. Consult the manufacturer’s recommendations and consider factors such as temperature, speed, and load.
- Lubricant Application: Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for lubricant application, whether it involves manual or automated systems. Ensure proper distribution of lubricant to minimize friction and wear.
- Regular Greasing: Establish a regular greasing schedule to maintain optimum lubrication levels. Insufficient lubrication can lead to increased friction, excessive heat, and premature component failure.
- Filter Maintenance: Keep the lubrication system’s filters clean and functional. Clogged filters can impede the flow of lubricant and compromise the system’s effectiveness.
Cleaning and Debris Removal:
The accumulation of debris, dust, and contaminants can hinder the performance of a ball mill. Regular cleaning and debris removal not only improve efficiency but also prevent potential equipment damage.
Cleaning:
Clean the ball mill internals, such as the grinding chamber, liners, and diaphragms, to remove built-up material and residues. Use appropriate cleaning agents and methods recommended by the manufacturer. Be cautious when cleaning sensitive parts to avoid causing any damage.
Debris Removal:
Regularly remove debris, such as grinding media particles, from the mill. These particles can accumulate in the discharge system, leading to clogs and reduced efficiency. Use suitable methods, such as vacuuming or compressed air, to remove debris and maintain optimal operation.
Wear Parts Replacement
Ball mills consist of several wear-prone components that require regular inspection and replacement. Some of the critical parts include mill liners, grinding media, and trunnion bearings. Here are some maintenance practices to consider:
- Liner Inspection and Replacement: Inspect mill liners regularly for signs of wear, such as excessive erosion, cracks, or loose bolts. Replace worn liners promptly to prevent damage to the mill shell and optimize grinding efficiency.
- Grinding Media Monitoring: Monitor the condition and wear of grinding media, such as balls or rods. Replace worn or damaged media to ensure consistent and efficient grinding performance.
- Trunnion Bearing Maintenance: Regularly inspect trunnion bearings for signs of wear or damage, such as overheating, excessive noise, or loss of lubrication. Timely replacement or repair of trunnion bearings can prevent costly breakdowns and extend the life of the equipment.
Alignment and Balance:
Proper alignment and balance are critical for the smooth operation and longevity of a ball mill. Misalignment or imbalance can lead to excessive vibrations, premature wear, and decreased overall performance.
Alignment:
Regularly check and adjust the alignment of the mill components, including the pinion, girth gear, and motor. Misalignment can cause uneven wear on gears and lead to excessive noise and vibrations. Consult the manufacturer’s guidelines for proper alignment procedures.
Balance:
Imbalance in rotating components, such as the grinding chamber or the grinding media, can cause severe vibrations. Ensure that the mill is properly balanced and that the load distribution is even. Unbalanced conditions should be corrected promptly to avoid equipment failure and minimize maintenance requirements.
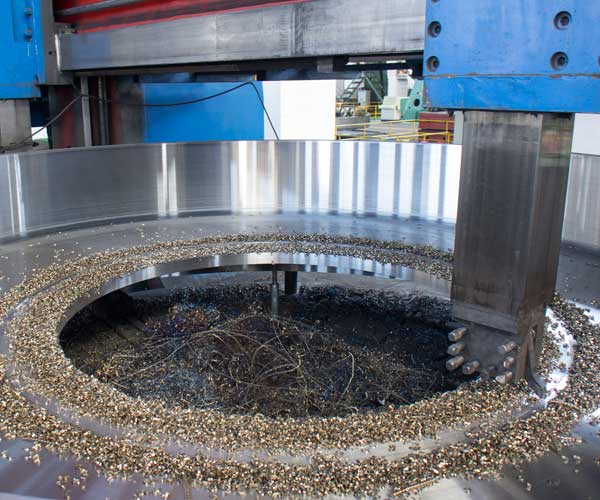

Ball Mill Maintenance Cycle: Ensuring Longevity and Efficiency
To ensure continuous performance and avoid costly downtime, it is crucial to establish a well-defined maintenance cycle for ball mills.
The Significance of Ball Mill Maintenance:
Regular maintenance of ball mills is vital for several reasons:
- Equipment Longevity: Ball mills are subjected to harsh operating conditions, such as high temperatures, heavy loads, and abrasive materials. Without proper maintenance, these factors can lead to wear and tear, reducing the equipment’s lifespan.
- Production Efficiency: Even minor issues or malfunctions in a ball mill can result in reduced efficiency, increased energy consumption, and decreased product quality. Maintenance helps identify and rectify problems before they escalate, ensuring consistent and efficient operations.
- Cost Savings: Implementing a well-structured maintenance plan reduces the likelihood of unexpected breakdowns and subsequent production stoppages. This proactive approach minimizes repair costs, avoids emergency purchases, and optimizes the utilization of maintenance resources.
Recommended Maintenance Schedule:
To establish an effective maintenance cycle for ball mills, the following schedule is recommended:
- Daily Inspections: Conduct visual inspections to identify any obvious signs of wear, leaks, or abnormal noise. Check lubrication levels and ensure safety features are in place.
- Weekly Maintenance: Clean the mill, inspect and clean the grates, and check lubrication systems. Inspect liners and grinding media for wear and replace if necessary.
- Monthly Inspections: Perform more detailed inspections, focusing on critical components like trunnion bearings, gears, and drive systems. Conduct alignment checks and inspect electrical systems.
- Semi-Annual Maintenance: Plan comprehensive maintenance during production shutdowns. This includes a thorough inspection of all components, replacement of worn-out parts, lubrication system overhaul, and realignment if required.
- Annual Maintenance: Conduct an in-depth inspection of the entire mill, including non-destructive testing, to detect any structural issues or weaknesses. Evaluate and update maintenance procedures based on the mill’s performance and manufacturers’ recommendations.
Best Practices for Ball Mill Maintenance:
In addition to following a regular maintenance cycle, the following best practices will further enhance the longevity and efficiency of ball mills:
- Training and Documentation: Provide comprehensive training to maintenance personnel on the proper operation and maintenance of ball mills. Maintain detailed records of maintenance activities, including inspections, repairs, and component replacements.
- Collaboration with Manufacturers: Establish a strong relationship with ball mill manufacturers to stay updated on maintenance best practices, technical advancements, and recommended spare parts. Seek their guidance for complex maintenance tasks or when encountering unusual issues.
- c) Predictive Maintenance Techniques: Implement predictive maintenance techniques, such as vibration analysis, thermography, and oil analysis, to identify potential problems before they lead to equipment failure. This proactive approach minimizes unplanned downtime and reduces repair costs.
- d) Continuous Improvement: Regularly review and improve maintenance procedures based on equipment performance, operational feedback, and emerging industry standards. Encourage maintenance teams to provide input and suggestions for optimizing maintenance practices.
Operational and Safety Considerations
In addition to regular maintenance practices, there are several operational and safety considerations that should be prioritized:
- Operating Parameters: Monitor and optimize operating parameters such as mill speed, feed rate, and solids concentration. Operating outside the recommended ranges can lead to reduced efficiency, increased wear, and potential equipment damage.
- Safety Inspections: Regularly conduct safety inspections to identify and address potential hazards. Ensure proper guarding, emergency stop systems, and lockout/tagout procedures are in place to protect personnel and prevent accidents.
- Operator Training: Provide comprehensive training to operators to ensure they understand the equipment’s operation, maintenance procedures, and safety protocols. Well-trained operators can detect early warning signs and take appropriate actions to prevent costly breakdowns.
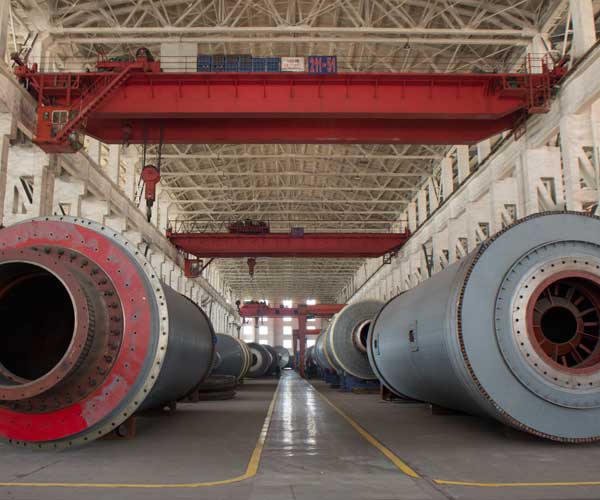

How to Mount a Ball Mill
Mounting a ball mill is a critical step in the process of preparing materials for various industrial applications. Whether you are a seasoned professional or an amateur, understanding the proper procedure for mounting a ball mill is crucial to ensure its optimal performance and longevity.
Safety First:
Before initiating the mounting process, prioritize safety measures to protect yourself and others involved. Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as safety glasses, gloves, and steel-toe boots. Make sure the work area is clean and free from any potential hazards. Additionally, familiarize yourself with the specific safety guidelines provided by the manufacturer of the ball mill.
Planning and Preparation:
A well-structured plan is essential for a successful ball mill mounting process. Consider the following aspects before proceeding:
- Site Evaluation: Evaluate the site where the ball mill will be mounted. Ensure that it provides adequate space for the mill, proper ventilation, and convenient access for maintenance and operation.
- Foundation Design: Consult engineering experts to design a solid foundation that can withstand the weight and vibrations produced by the ball mill. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for foundation specifications.
- Equipment and Tools: Gather all the necessary equipment and tools required for the mounting process. This typically includes lifting equipment, wrenches, leveling devices, and measuring tools.
Lifting and Positioning:
Moving and positioning the ball mill require careful attention to prevent accidents and damage to the equipment. Follow these steps:
- Use Lifting Equipment: Employ appropriate lifting equipment such as cranes, forklifts, or hoists to lift the ball mill. Ensure that the lifting capacity of the equipment is suitable for the weight of the mill.
- Secure the Load: Attach suitable lifting slings or straps securely to the mill. Distribute the weight evenly to maintain stability during lifting.
- Positioning: Slowly and cautiously move the ball mill to the desired location. Align it with the foundation markings and verify that it is level.
Foundation Installation:
Installing a sturdy foundation is crucial for the long-term stability and performance of the ball mill. Follow these steps for a successful foundation installation:
- Clear the Area: Remove any debris, dirt, or loose materials from the foundation site.
- Excavation: Excavate the foundation according to the specified dimensions provided by the engineering experts. Ensure the depth and width are sufficient to accommodate the foundation design.
- Reinforcement: Install any necessary reinforcement bars or steel meshes according to the engineering design to enhance the strength of the foundation.
- Pouring Concrete: Prepare the concrete mixture following the recommended guidelines. Pour the concrete into the foundation pit, ensuring it reaches all corners and edges. Use a vibrating tool to eliminate air pockets and ensure uniformity.
- Curing and Drying: Allow sufficient time for the concrete to cure and dry. Follow the curing instructions provided by the concrete manufacturer, which typically involve watering and covering the foundation to maintain appropriate moisture levels.
Final Adjustments and Testing:
Once the ball mill is mounted on the foundation, perform the following adjustments and tests:
- Leveling: Use precision leveling devices to ensure the ball mill is perfectly level. Adjust the foundation or use shims as necessary.
- Alignment: Verify that the ball mill is aligned with other connected equipment, such as gearboxes or motor couplings. Misalignment can cause excessive wear and reduce operational efficiency.
- Test Run: Before starting regular operations, perform a test run of the ball mill. Gradually increase the speed and observe any abnormal vibrations or noises. Address any issues before proceeding with full-scale operation.
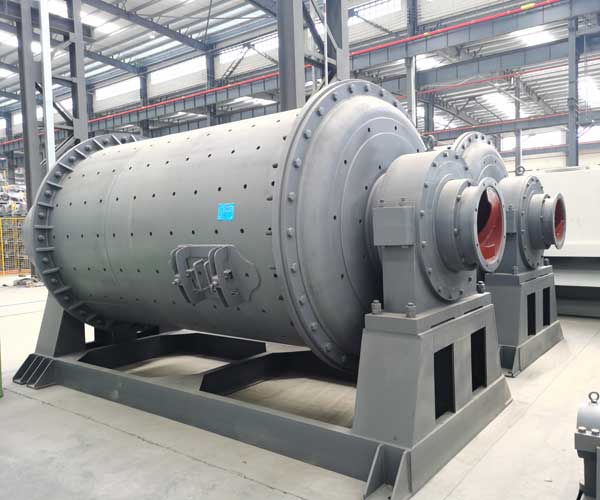

How to Start a Ball Mill
The operation of a ball mill requires careful attention and knowledge to ensure its safe and efficient startup.
Read the Manual and Familiarize Yourself
Before starting any machinery, it is crucial to read the manufacturer’s manual thoroughly. The manual contains specific instructions, safety guidelines, and maintenance procedures for your ball mill. Familiarize yourself with the components, controls, and operational requirements to ensure a smooth startup process.
Check for Proper Installation and Connections
Ensure that the “>ball mill is installed correctly, following the manufacturer’s guidelines. Check the foundation, alignment, and levelness of the mill. Inspect all the connections, including electrical wiring, lubrication systems, and cooling mechanisms, to verify that everything is properly connected and in good condition.
Inspect and Prepare the Mill
Before starting the ball mill, conduct a visual inspection to identify any potential issues or damages. Check for loose bolts, leaks, excessive vibration, or unusual noises. Ensure that the mill’s interior is clean and free from debris, as foreign objects can damage the mill or affect its performance.
Pre-Startup Safety Measures
Safety should always be a priority when starting any equipment, including ball mills. Take the following precautions:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Wear appropriate PPE, including safety glasses, gloves, and hearing protection, to protect yourself from potential hazards.
- Lockout/Tagout: Implement proper lockout/tagout procedures to prevent accidental startup. Disconnect the power supply and secure it with a lock and tag to ensure no one can energize the system during maintenance or startup.
- Ventilation: Ensure that the mill area is well-ventilated to prevent the accumulation of harmful gases or fumes.
- Fire Safety: Have fire extinguishers readily available in case of emergencies. Familiarize yourself with the location and proper use of fire extinguishers.
Start-Up Procedure
Once you have completed the necessary safety measures, you can proceed with the following start-up procedure:
- Start with a Low Power Setting: Initially, set the mill to a low power setting to allow a gradual acceleration of the rotational speed. This helps reduce stress on the components and minimizes the chances of overloading the motor.
- Check Rotation Direction: Verify that the mill rotates in the correct direction. Most ball mills have an arrow indicating the rotation direction. Ensure that the rotation matches the arrow to prevent damage to the mill or its components.
- Gradually Increase the Speed: Increase the rotational speed gradually, allowing the mill to reach the desired operating speed. Sudden speed changes can cause excessive stress on the mill’s components.
- Monitor the Operation: Pay close attention to the mill’s operation during startup. Observe for any abnormal vibrations, excessive noise, or unusual temperature increases. If any issues arise, immediately shut down the mill and investigate the cause before proceeding.
Post-Startup Checks
After successfully starting the ball mill, perform the following checks:
- Lubrication: Verify that the lubrication system is functioning correctly. Check oil levels and ensure proper lubrication to prevent excessive wear and tear.
- Temperature Monitoring: Monitor the temperature of the bearings, gears, and motor during operation. Abnormally high temperatures can indicate problems and should be investigated promptly.
- Check for Leaks: Regularly inspect for leaks in the cooling or lubrication systems. Address any leaks immediately to avoid equipment damage and ensure optimal performance.