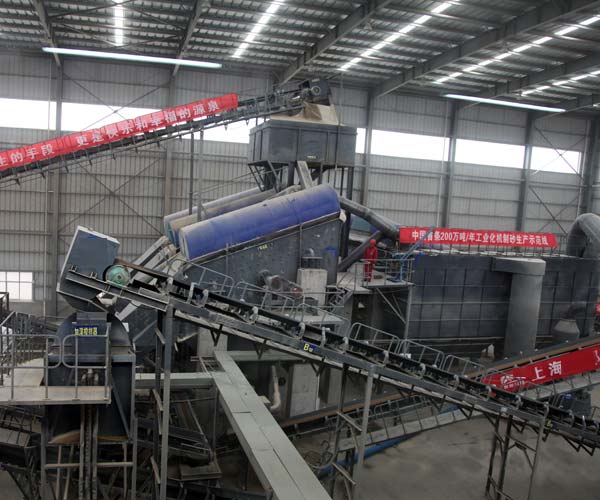
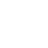
The sand making production line, a sophisticated and innovative system, efficiently converts rocks into sand. By turning rocks into sand, this sophisticated process ensures a sustainable supply of high-quality sand for construction and industrial applications.
24 Online Service

Sand serves as a fundamental building material, playing a vital role in the creation of concrete, asphalt, and various construction projects. With the ever-increasing pressure to meet these demands while adhering to environmental sustainability, the sand making production line has emerged as a critical solution.
A sand making production line, also known as a sand production line or sand manufacturing plant, is a series of equipment used to produce artificial sand from raw materials like rocks, pebbles, and other aggregates. The process involves crushing large rocks into smaller particles, which are then processed to produce sand of varying sizes and shapes. This synthetic sand, also known as manufactured sand or M-sand, exhibits similar properties to natural sand but is specifically engineered to meet specific construction needs.
The process begins with the feeding system, where the raw materials, such as large rocks and pebbles, are fed into the crusher or sand making machine. This system ensures a continuous and uniform supply of raw materials to maintain efficiency in the production process.
The heart of the sand making production line lies in the crushing equipment. Various types of crushers, such as jaw crushers, impact crushers, or cone crushers, are used to break down the raw materials into smaller, manageable sizes. This comminution process is crucial as it influences the quality and shape of the final manufactured sand.
After the initial crushing stage, the crushed materials are further processed by the sand making machine. This specialized equipment uses the principles of centrifugal force and “stone-on-stone” crushing to reshape the particles, producing sand with improved gradation and texture.
The next phase involves the screening of the sand particles to ensure consistent size distribution. Screening equipment removes any oversized or undersized particles, providing a uniform and desirable end product.
To enhance the quality of the manufactured sand, a sand washing machine is employed. This process removes impurities, such as dust, clay, and silt, which may negatively impact the concrete’s strength and durability. Additionally, grading the sand according to specific particle sizes ensures it meets the required specifications for different construction applications.
Once the sand production is complete, the final product is stored in silos or storage facilities. Conveyors then transport the sand to its intended destination, ready for use in construction projects.
The sand making production line plays a crucial role in sustainable resource management. As natural sand reserves deplete and environmental concerns arise from excessive sand dredging from rivers and beaches, the utilization of manufactured sand becomes essential to preserve our natural resources.
By producing artificial sand in a controlled environment, the sand making production line ensures consistent quality and adherence to specific requirements. This consistency is vital for construction projects that demand uniformity in their materials, ultimately leading to better structural integrity and longevity.
In regions where natural sand is scarce or expensive, the use of manufactured sand can significantly reduce construction costs. Moreover, it curtails transportation expenses since sand production can be localized near the construction site.
A sand making production line can be tailored to suit different construction applications, accommodating a wide range of aggregate requirements. This adaptability allows for the creation of sand with varying textures, shapes, and sizes, making it suitable for specific uses such as concrete, asphalt, and road construction.
Traditional sand extraction from rivers and coastal areas poses substantial environmental risks, including erosion, loss of habitats, and disturbance to aquatic ecosystems. By using manufactured sand, the detrimental impact on the environment is minimized, allowing for more sustainable construction practices.
Aggregates are essential materials composed of crushed rocks, sand, and gravel, which serve as the backbone for constructing roads, buildings, bridges, and various other structures. Understanding the primary stages of this process is crucial for ensuring the delivery of high-quality aggregates that meet industry standards.
The journey of aggregates begins with the extraction of raw materials, which primarily consists of large rocks and boulders sourced from quarries or gravel pits. Before these materials can be utilized in construction, they must undergo the crushing stage. The primary objective of this stage is to reduce the size of the raw materials by breaking down large rocks into smaller, more manageable pieces.
Crushers, the workhorses of the crushing stage, come in various forms, such as jaw crushers, gyratory crushers, impact crushers, and cone crushers. Each type of crusher is designed to handle specific rock types, sizes, and hardness levels. For instance, jaw crushers excel at processing hard, abrasive rocks, while cone crushers are more suitable for softer materials.
The crushing process begins with feeding the rocks into the crusher’s chamber, where a rotating mantle or jaws apply pressure to break them down. The resulting smaller fragments, known as aggregates, vary in size depending on the specific requirements of the construction project. The crushed rocks are then transported to the next stage in the process: screening.
Upon exiting the crushing stage, the aggregates still contain a mixture of various sizes. The screening stage aims to segregate the crushed rocks into different size fractions, ensuring that each fraction meets the required specifications for the intended application. This process is achieved through the use of specialized equipment called screens.
Screens consist of a series of layers or decks with different-sized openings, allowing smaller aggregates to pass through while retaining larger ones. As the crushed rocks move along the screens, vibrations and gravity aid in the separation process. The resulting graded aggregates are then collected in individual stockpiles based on their sizes.
This sorting process is crucial, especially when it comes to projects with specific grading requirements. Different construction applications demand aggregates of varying sizes to achieve the desired structural integrity, stability, and aesthetic appearance. For example, fine aggregates are ideal for creating smooth concrete surfaces, while coarse aggregates are necessary for supporting heavy loads in road construction.
After the screening stage, it is common to further process certain aggregates through the washing stage. Washing is a critical process that involves the removal of impurities, such as silt, clay, dust, and organic matter, from the surface of the sand or crushed rock particles. It is particularly important for sand used in concrete and mortar production, as well as for creating high-quality asphalt mixes.
During the washing stage, the aggregates are mixed with water in a wash tank or screw washer. The water dislodges and carries away the unwanted impurities, leaving behind clean aggregates that meet the required quality standards. The washed aggregates are then dewatered and stockpiled for further use.
The importance of washing aggregates cannot be overstated. First and foremost, it ensures that the final product meets the necessary quality and performance specifications. Clean aggregates enhance the durability and strength of the concrete, providing a solid foundation for construction projects that can withstand the test of time and environmental factors.
Moreover, washing also helps to comply with environmental regulations. By removing harmful contaminants, the discharge of wastewater from the washing process becomes less environmentally detrimental. This is particularly relevant in areas with stringent water quality regulations or sensitive ecological surroundings.

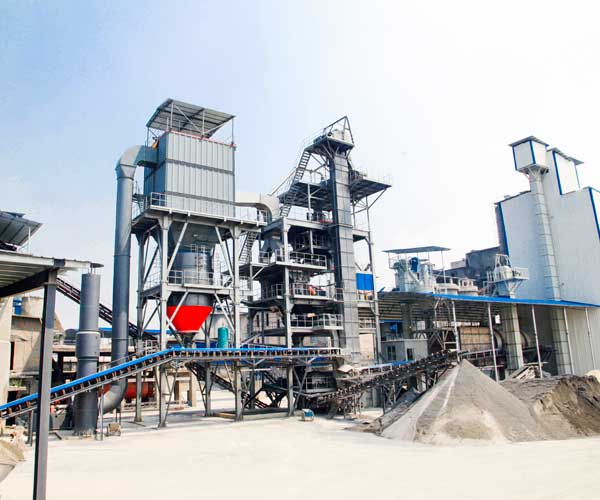
Sand Produced versatile properties make it an indispensable component in various industries, including construction, manufacturing, and beyond. The sand making production line plays a crucial role in producing different grades of sand, tailored to specific requirements.
The sand making production line is an advanced process that involves crushing, screening, washing, and shaping raw materials to create high-quality sand. This production line can be designed to produce various grades of sand based on specific requirements such as particle size, shape, and composition.
Fine sand, also known as masonry sand or play sand, is characterized by its small grain size and smooth texture. The sand making production line achieves this grade by using finer mesh screens during the screening process. Fine sand is often utilized in construction projects requiring a smooth finish, such as plastering, bricklaying, and sandblasting.
Coarse sand, with larger particle sizes, is ideal for applications where drainage and permeability are essential. The production line achieves this grade by using coarser mesh screens during the screening process. Coarse sand finds application in landscaping, road bedding, and concrete mixtures to enhance drainage capabilities and provide stability.
Washed sand is a grade obtained after washing impurities, clay, and silt from the raw material during the production process. This process ensures a clean, consistent, and high-quality product. Washed sand is widely used in the production of concrete, as it enhances its workability and strength, making it an essential component in the construction industry.
Crushed sand is obtained by crushing larger rocks and boulders into smaller particles. The sand making production line utilizes advanced crushing techniques to achieve this grade. Crushed sand is often used as a substitute for natural sand in concrete and mortar mixtures due to its superior binding properties.
Silica sand is composed of high-purity quartz grains and is a critical raw material in various industries. The production line extracts silica sand from natural deposits and is used in glass manufacturing, ceramics, electronics, and water filtration systems due to its high heat resistance and chemical inertness.
The sand making production line can also produce specialty sands tailored for specific applications. Examples include foundry sand, used in metal casting, and sports field sand, designed to improve the playing surface and drainage on sports fields.
The construction industry is the largest consumer of sand, utilizing various grades for different purposes. Fine sand is extensively used for plastering walls and creating a smooth surface for decorative finishes. Coarse sand is employed as a bedding material for roads and foundations, promoting drainage and stability. Washed sand is vital in concrete and mortar production, providing workability and strength, while crushed sand serves as a sustainable alternative to natural sand in construction materials.
Sand plays a crucial role in numerous manufacturing processes. Silica sand, with its high heat resistance, is used in glass manufacturing to produce bottles, windows, and various glassware. The electronics industry relies on silica sand to create molds for casting metal and producing silicon chips. Additionally, specialty sands find application in foundries for creating molds and cores in metal casting processes.
Beyond construction and manufacturing, sand is indispensable in several environmental applications. Permeable pavement systems, commonly used to manage stormwater runoff, incorporate coarse sand to allow water infiltration and reduce runoff. Silica sand’s high porosity makes it an excellent material for water filtration systems, removing impurities and purifying drinking water.
The sports industry relies on specialty sands to improve playing surfaces and promote athlete safety. Sports field sand, composed of specific grain sizes, enhances the drainage properties of playing fields, preventing waterlogging and providing a safer playing environment. Additionally, sand is used in the construction of golf course bunkers, beach volleyball courts, and children’s playgrounds.
Our Projects
Copyright © ZENITH, All Right Reserved.