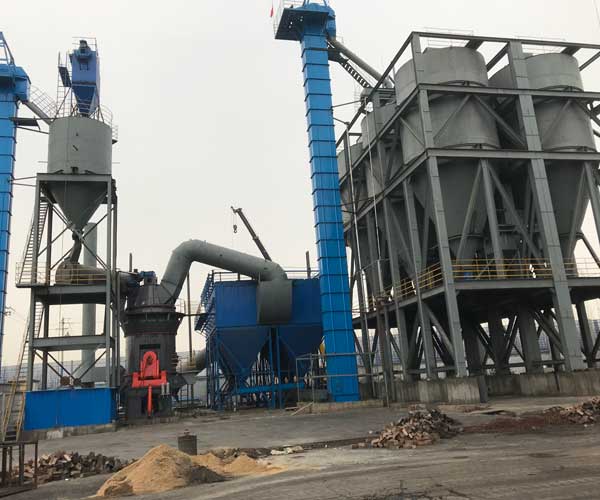
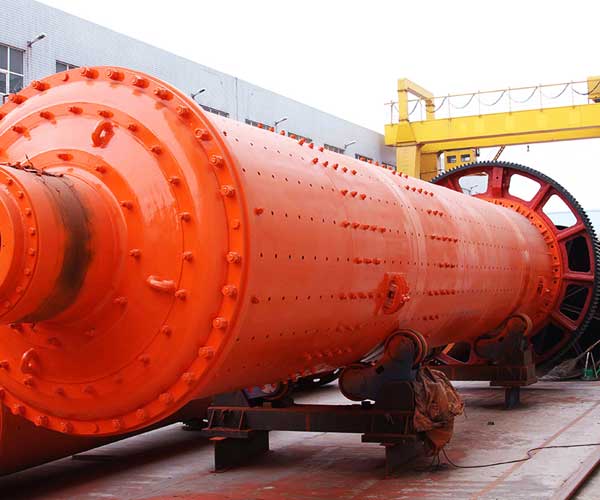
What type of Coal Mill In A Thermal Power Plant
Types of Coal Mills in Thermal Power Plants
The choice of a coal mill depends on various factors, such as the type of coal, grindability, and the desired fineness of the output. The most common types of coal mills used in thermal power plants are:
-

In a ball mill, coal is crushed between steel balls and a rotating horizontal cylinder. As the cylinder rotates, the balls are lifted and fall onto the coal, breaking it into smaller particles. The fine coal powder is carried by primary air to the boiler for combustion. This type of mill is known for its ability to handle various coal types and produce consistent particle sizes.
-

A vertical mill, commonly known as a bowl mill, consists of a vertical spindle that rotates a grinding bowl filled with coal. Grinding rollers press against the bowl, crushing the coal into a fine powder. The crushed coal is then carried by primary air to the boiler for combustion. This type of mill is widely used due to its reliability, low maintenance requirements, and efficient performance.
Functions of Coal Mills in Thermal Power Plants
Coal mills play a crucial role in the overall process of coal-fired power plants, performing the following functions:
- Grinding: Coal mills grind raw coal into a fine powder, which increases the surface area and allows for more efficient combustion in the boiler.
- Drying: As coal mills grind the raw coal, they also remove moisture from it. The drying process is essential for high-moisture coals, as it improves combustion efficiency and reduces the risk of boiler slagging.
- Classification: In some coal mills, a classifier separates fine and coarse coal particles. The fine particles are carried to the boiler for combustion, while the coarse particles are returned to the mill for further grinding.
- Transport: Coal mills transport the fine coal powder to the boiler through primary air, which is heated to remove moisture and improve combustion efficiency.
Factors Affecting Coal Mill Efficiency
The efficiency of coal mills in thermal power plants is influenced by several factors, including:
- Coal Properties: The grindability, moisture content, and volatile matter of coal affect its behavior in the mill and the resulting particle size distribution.
- Mill Settings: The operational settings, such as mill speed, grinding pressure, and air-to-fuel ratio, influence the performance of coal mills.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance of coal mills, including inspection of grinding elements, lubrication of moving parts, and timely replacement of worn-out components, is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and efficiency.
- Classifier Performance: The efficiency of the classifier determines the particle size distribution of the output, which impacts combustion efficiency in the boiler.
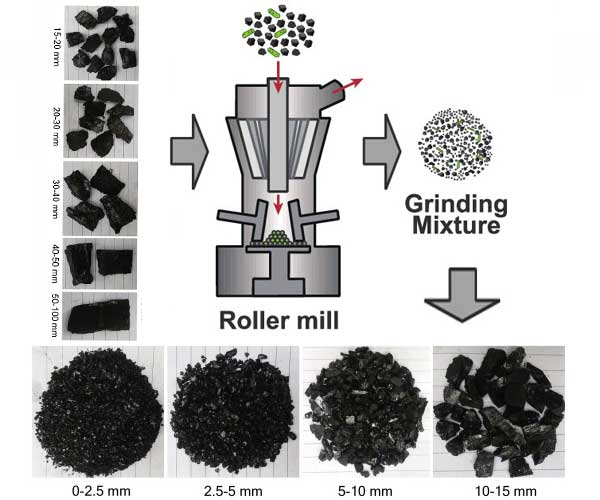
What size of coal is used in Thermal power plant
Coal Size in Thermal Power Plants
Coal-fired thermal power plants generate a significant portion of the world’s electricity. To optimize combustion efficiency and reduce emissions, it is essential to understand the importance of coal size and how it impacts the performance of a power plant.
Typical Coal Size in Thermal Power Plants
In a coal-fired power plant, raw coal is crushed and ground into a fine powder, known as pulverized coal. This fine powder is then burned in the boiler to generate steam, which drives turbines to produce electricity. The optimal coal size for efficient combustion in a thermal power plant is generally in the range of 70 to 100 microns (0.0028 to 0.0039 inches). However, the actual size distribution may vary depending on factors such as the type of coal, the pulverizing system used, and the desired fineness of the output.
Significance of Optimal Coal Particle Size
Achieving the optimal coal particle size is crucial for the overall efficiency and performance of a thermal power plant, as it influences:
- Combustion Efficiency: Smaller coal particles have a larger surface area, allowing for more efficient combustion in the boiler. This results in more heat being released from the coal, which in turn improves the overall efficiency of the power plant.
- Emissions: Optimal coal particle size can help reduce emissions from the power plant. Smaller coal particles burn more completely, which reduces the amount of unburned carbon and other pollutants released into the atmosphere.
- Boiler Performance: The size of coal particles can impact the performance of the boiler. Larger coal particles may not burn completely, leading to the formation of slag deposits on boiler surfaces. These deposits can reduce heat transfer efficiency and may require costly maintenance to remove.
- Fly Ash Quality: The size of coal particles can also affect the quality of fly ash, a byproduct of coal combustion that is collected and used in various applications, such as cement production and road construction. Smaller coal particles typically result in finer fly ash with better pozzolanic properties, making it more suitable for use in these applications.
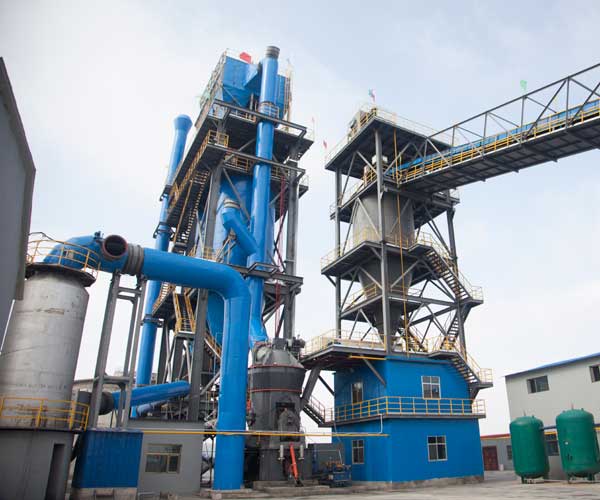

How Does A Coal Mill In A Thermal Power Plant Work
Coal mills play a crucial role in coal-fired thermal power plants, as they process raw coal into a fine powder, known as pulverized coal, which is used as fuel in the boiler to generate steam and electricity.
The Purpose of a Coal Mill in a Thermal Power Plant
In a coal-fired power plant, the coal mill serves the following purposes:
- Grinding: The primary function of the coal mill is to grind raw coal into a fine powder, which increases its surface area and allows for more efficient combustion in the boiler.
- Drying: Coal mills also remove moisture from the raw coal, improving combustion efficiency and reducing the risk of boiler slagging.
- Transportation: Coal mills transport the pulverized coal to the boiler through primary air, which is heated to remove moisture and improve combustion efficiency.
Primary Components of a Coal Mill
Coal mills in thermal power plants consist of several key components, including:
- Coal Feeder: The coal feeder supplies a continuous stream of raw coal to the mill. It regulates the flow of coal based on the demand from the boiler and maintains a consistent coal-to-air ratio for efficient combustion.
- Grinding Table: The grinding table is a rotating horizontal surface that holds the raw coal and grinding elements, such as balls or rollers, in a vertical spindle mill. The coal is crushed as the grinding elements press against it.
- Grinding Elements: Grinding elements, such as balls, rollers, or beater plates, are responsible for crushing the raw coal into a fine powder. Their shape, size, and material can impact the efficiency of the coal mill.
- Classifier: In some coal mills, a classifier separates fine and coarse coal particles. The fine particles are carried to the boiler for combustion, while the coarse particles are returned to the mill for further grinding.
- Primary Air: Primary air is heated and then mixed with the pulverized coal to transport it to the boiler. The temperature, flow rate, and distribution of primary air can impact coal mill performance and the quality of the pulverized coal.
The Coal Pulverization Process
The coal pulverization process in a coal mill can be summarized in the following steps:
- Feeding: Raw coal is fed into the mill by the coal feeder, which regulates the flow based on the demand from the boiler.
- Grinding: As the grinding table rotates, raw coal is crushed by the grinding elements, breaking it into smaller particles. The grinding process also dries the coal, removing moisture and improving combustion efficiency.
- Classification: In mills with classifiers, the pulverized coal is separated by particle size. Fine particles are carried by primary air to the boiler for combustion, while coarse particles are returned to the mill for further grinding.
- Transportation: The fine pulverized coal is mixed with heated primary air and transported to the boiler for combustion.
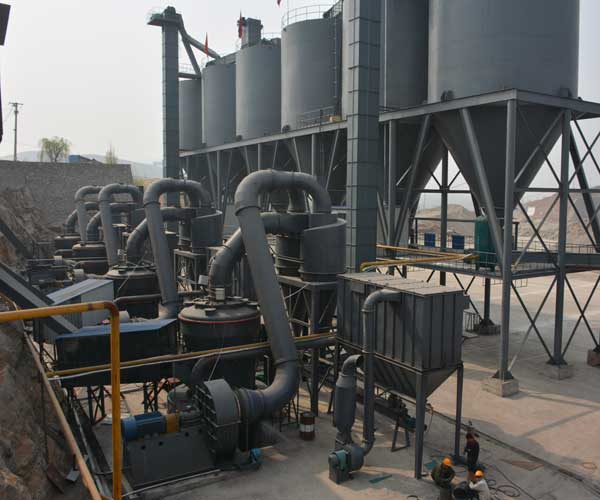

Coal Grinding Mill: The Heart of a Thermal Power Plant
In the rapidly evolving energy landscape, the coal grinding mill remains a key component of a thermal power plant. Despite the growth of renewable energy sources and the increasing focus on reducing carbon emissions, coal-fired power plants continue to be a significant contributor to global electricity generation. The coal grinding mill, as the heart of a thermal power plant, plays a critical role in ensuring the efficiency and reliability of the plant’s operation.
Coal Preparation: A Crucial Step
Before coal can be used as a fuel source in a thermal power plant, it must first be processed to meet the required specifications. The coal is typically delivered to the plant in its raw form, which contains a mix of coal, rocks, and other impurities. The first step in the process involves crushing the coal to a manageable size, followed by the removal of unwanted materials. This is where the coal grinding mill comes into play.
The Role of the Coal Grinding Mill
The coal grinding mill is designed to pulverize raw coal into a fine powder, which can be more easily burned and produce less pollution. This is achieved by using large, rotating steel balls or rollers to crush the coal into a fine dust. The coal grinding mill operates under immense pressure and temperature, requiring robust and reliable construction to withstand the harsh environment.
Grinding mills are available in various sizes and designs, with each model tailored to suit the specific requirements of a given thermal power plant. The selection of the appropriate coal grinding mill depends on factors such as the type of coal used, the desired fineness of the end product, and the plant’s capacity.
Improving Efficiency and Reducing Emissions
The efficiency of a coal grinding mill is critical in determining the overall efficiency of a thermal power plant. The more efficiently the coal can be ground, the less energy is required to convert it into electricity. This not only reduces the plant’s fuel consumption but also minimizes the associated emissions of carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, and other harmful pollutants.
Modern coal grinding mills incorporate various technological advancements to improve efficiency and reduce emissions. Some of these innovations include:
- Dynamic classifiers: These devices are used to separate the coal particles by size, ensuring that only the finest particles are sent to the boiler for combustion. This results in more efficient burning and reduced emissions.
- High-efficiency roller mills: Roller mills are known for their superior grinding performance compared to traditional ball mills. They consume less energy and produce a finer coal dust, which translates to improved combustion efficiency and reduced emissions.
- Computerized control systems: Advanced control systems monitor and adjust the coal grinding process in real-time, optimizing performance and minimizing energy consumption. These systems can also help identify potential issues, allowing for proactive maintenance and reducing the risk of unplanned downtime.
- Improved wear-resistant materials: The use of wear-resistant materials in the construction of the coal grinding mill helps to prolong its service life and minimize the need for frequent maintenance.
As the global energy landscape continues to evolve, the role of coal-fired power plants is expected to decline. However, coal is still an abundant and relatively inexpensive fuel source, and many countries, particularly in the developing world, continue to rely on coal-fired power plants for electricity generation.
Coal Grinding Mill Projects in China, Vietnam
-

300,000TPY Clean Coal Grinding Plant
Project Site: Gansu, China
Equipment: 1 LM220 Vertical Mill, dust collector, fan, nitrogen protection system, fire extinguishing device and intelligent centralized control device
Material: Coal Input Size: ≤40mm
Output Size: 200meshes (0.074mm), D80
Capacity:300,000TPY
-
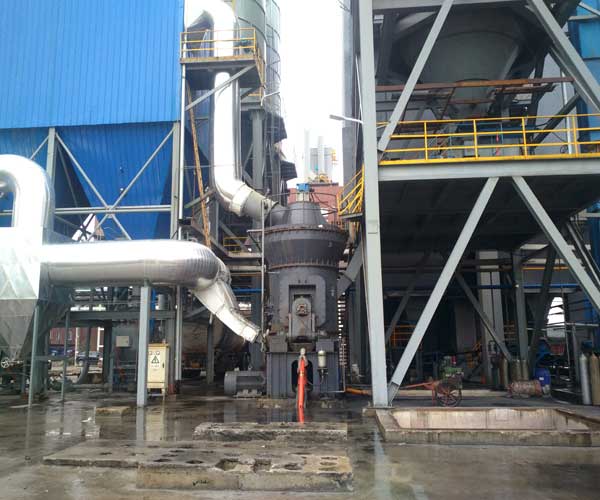

20TPH Coal Grinding Plant
Raw Material:Coal, semi-coke,bituminous mixture
Capacity: ≥20TPH
Input Size: ≤20mm
Output Size: 200 mesh 90D
Equipment: LM Vertical Grinding Mill, enclosed feeder, electric control cabinet
-

30TPH Clean Coal Powder Preparation Plant
Material: Coal Powder
Capacity: 30TPH
Output Size: 200mesh
Equipment: 2 sets of LM150A Vertical Grinding Mills
Application: Supplied to boilers for heating
-
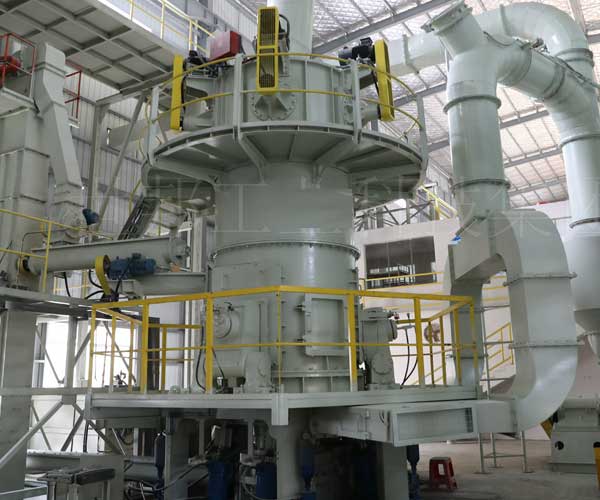

Vietnam 15TPH Coal Grinding Plant
Project Site: Vietnam
Customer: A famous non-metallic ore supplier in local area
Equipment: Complete set of LM130M system
Material: Coal
Capacity: 15TPH
Date of Operation: October, 2015