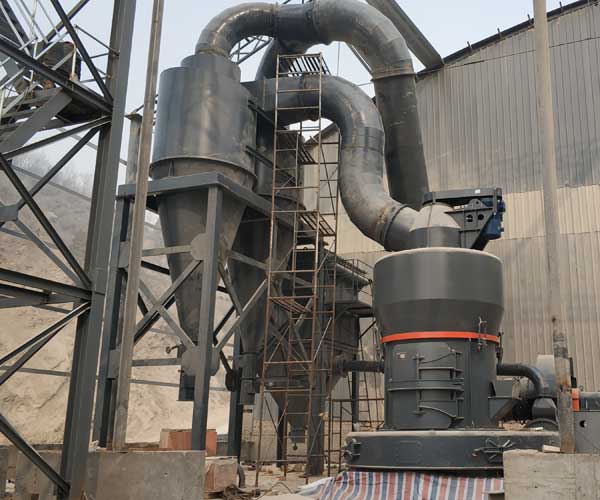
Zircon sand mill machines have revolutionized the sand processing industry by providing enhanced efficiency, precision, and productivity. These advanced machines enable manufacturers to achieve better control over particle size distribution, improve processing speed, ensure uniformity, and reduce costs.
24 Online Service

Zircon sand, also known as zirconium silicate (ZrSiO4), owes its existence to geological processes that span millions of years. It is a naturally occurring mineral, commonly found in igneous and metamorphic rocks. The formation of zircon sand begins when magma cools and crystallizes deep within the Earth’s crust. Over time, erosion and weathering expose these crystalline structures, freeing zircon grains that eventually find their way into sedimentary deposits.
Zircon sand exhibits a range of fascinating physical properties that contribute to its allure. In its purest form, zircon sand is colorless and transparent, but it can also appear in shades of yellow, orange, brown, and even green due to impurities. What sets zircon sand apart is its exceptional hardness, ranking around 7.5 on the Mohs scale, making it a durable gemstone that can withstand the test of time.
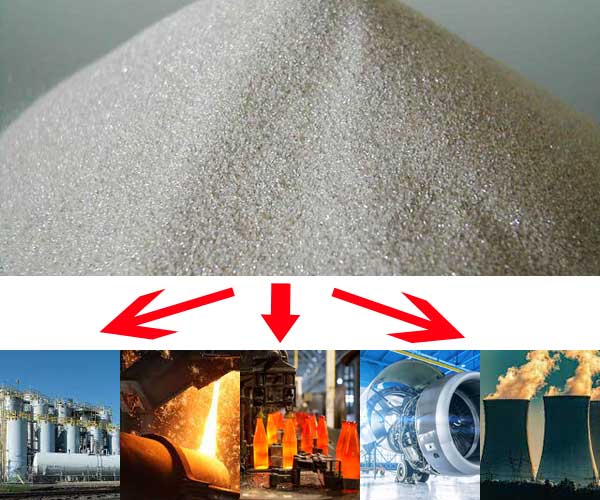
Zircon sand, derived from the mineral zirconium silicate, is a valuable resource known for its versatile properties. This unique material has found its way into a wide range of applications across various industries. From aerospace to nuclear energy, zircon sand plays a vital role due to its exceptional heat resistance, chemical stability, and electrical conductivity.
Zircon sand’s remarkable heat resistance and chemical stability make it an ideal ingredient in the production of refractory materials. Foundries, where metals are melted and shaped, rely on zircon sand as a key component in refractory coatings and molds. The high melting point of zircon sand, coupled with its low thermal expansion, allows it to withstand extreme temperatures and protect the molds during the casting process. Moreover, zircon sand’s resistance to chemical corrosion ensures durability and longevity, making it an essential material in foundry applications.
Zircon sand is widely used in the ceramics and glass industry, primarily due to its ability to enhance the properties of these materials. When added to ceramic glazes, zircon sand increases the strength and hardness of the finished products. It also provides a bright white color, improving the aesthetic appeal. In the glass industry, zircon sand acts as a fluxing agent, lowering the melting point and enhancing the clarity of glass. It also helps to improve the chemical resistance of glass, making it suitable for demanding applications such as laboratory equipment and fiber optics.
Zircon sand’s exceptional resistance to radiation and heat makes it an indispensable material in the nuclear energy sector. Zirconium, derived from zircon sand, is used to produce zirconium alloy tubes that encase nuclear fuel rods. These tubes, known as Zircaloy, provide a protective barrier, preventing the release of radioactive materials. Zirconium’s low neutron absorption cross-section also allows efficient energy production in nuclear reactors. Furthermore, zirconium oxide, a byproduct of zircon sand processing, serves as a thermal barrier coating in nuclear reactor components.
In the chemical industry, zircon sand finds application in various processes. Zirconium compounds derived from zircon sand, such as zirconium dioxide (zirconia), are used as catalysts in chemical reactions. Zirconium chemicals also serve as a component in paints, coatings, and adhesives, providing corrosion resistance and improving durability. Additionally, zircon sand’s electrical conductivity makes it valuable in the production of fuel cells and solid oxide electrolysis cells, aiding in the advancement of clean energy technologies.
Zircon sand’s properties make it valuable in aerospace and defense applications. The material’s high melting point and resistance to thermal shock make it suitable for use in thermal barrier coatings on aircraft engine components. These coatings protect against extreme temperatures and enhance engine efficiency. Zircon sand is also utilized in aerospace alloys, contributing to the lightweight and high-strength properties required for aircraft and spacecraft construction.
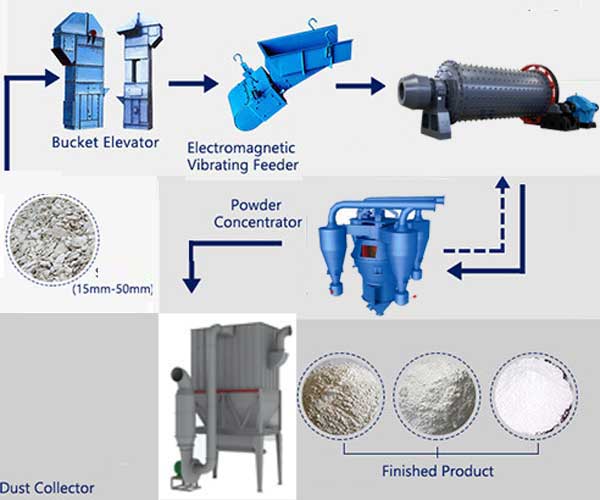

The processing of zircon sand involves a series of steps to extract and refine the mineral. The primary objective of this process is to obtain zirconium in its purest form for use in diverse applications.
Zircon sand primarily occurs in beach and dune deposits, often alongside other heavy minerals like ilmenite and rutile. The extraction of zircon sand begins with mining operations, where the mineral-rich sand is carefully excavated from the earth using heavy machinery. The sand is usually dredged from coastal areas or extracted from inland deposits through open-pit mining.
Once the zircon sand is obtained, it undergoes several processing stages to remove impurities and enhance its quality for various applications.
Purification of zircon sand is a crucial step to ensure its suitability for different industries. The primary impurities in zircon sand are typically composed of minerals like garnet, tourmaline, and monazite, which need to be removed to achieve a high-grade zircon product.
The purification process typically involves physical and chemical beneficiation techniques. Physical techniques, such as gravity separation, magnetic separation, and electrostatic separation, are employed to separate zircon sand from the accompanying heavy minerals. These techniques exploit the differences in density, magnetic susceptibility, and electrical conductivity of the minerals, allowing their efficient separation.
Chemical beneficiation methods, such as leaching and acid digestion, are employed to dissolve and remove impurities from zircon sand. The choice of purification method depends on the specific impurities present and the desired quality of the final product.
Once purified, the zircon sand is subjected to drying and milling processes. Drying removes any residual moisture from the sand, ensuring stability during subsequent processing steps. Milling involves grinding the dried zircon sand into a fine powder, which increases its surface area and facilitates further chemical reactions or blending with other materials.
The refined zircon sand can be further processed to obtain zirconium compounds or used directly in various applications. One of the primary uses of zirconium is in the production of zirconium dioxide (ZrO2), commonly known as zirconia. Zirconia exhibits exceptional hardness, thermal resistance, and electrical conductivity, making it valuable in the manufacturing of ceramics, refractories, and electrical components.
Zircon sand can also be processed to obtain zirconium sponge, which serves as a precursor for zirconium metal production. Zirconium metal finds applications in the aerospace industry, nuclear reactors, and various corrosion-resistant alloys.
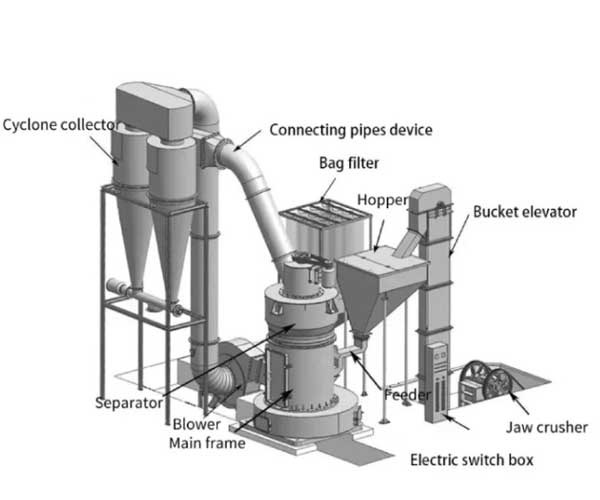
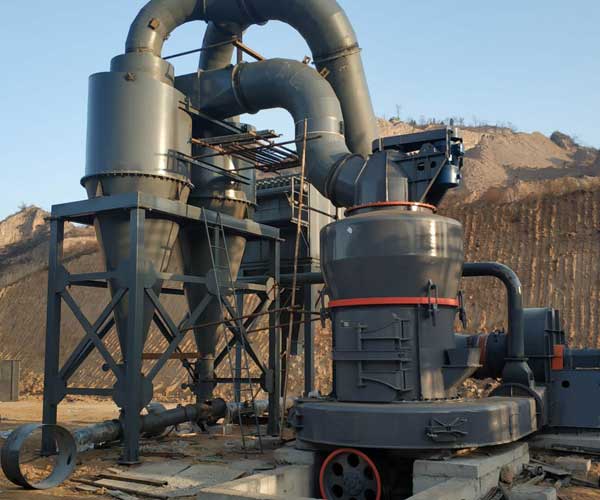
In the field of materials processing and manufacturing, grinding is an essential process that plays a crucial role in achieving precise and uniform particle sizes. When it comes to grinding abrasive materials like zircon sand, it becomes even more critical to employ specialized machines that can handle the challenges posed by such materials.
Grinding zircon sand presents several challenges that require careful consideration during the selection of grinding machines. One of the primary challenges is the material’s high hardness, which makes it difficult to achieve efficient grinding with conventional grinding methods. Zircon sand is known to cause significant wear and tear on grinding media, leading to higher maintenance costs and reduced productivity.
Another challenge is the abrasive nature of zircon sand particles, which can cause excessive heat generation during grinding. This can result in thermal damage to both the grinding media and the material being processed, leading to suboptimal grinding performance and reduced product quality.
Wet grinding machines offer a solution to overcome the challenges associated with grinding zircon sand. Unlike dry grinding, which relies on air flow and impact to break down particles, wet grinding employs the use of liquid media to facilitate the grinding process. This method provides several distinct advantages:
Wet grinding machines are designed to effectively reduce the particle size of zircon sand. The liquid media acts as a lubricant, reducing friction and heat generation, which in turn leads to improved grinding efficiency. By utilizing the liquid media, the grinding process can be carried out at lower speeds while achieving finer particle sizes, resulting in enhanced productivity and reduced energy consumption.
The use of wet grinding machines helps mitigate the abrasive wear caused by zircon sand. The liquid media acts as a protective layer, reducing the direct contact between the grinding media and the abrasive material. This leads to a longer lifespan for the grinding media, minimizing downtime and maintenance costs associated with frequent replacements.
Wet grinding machines enable precise control over the particle size distribution of the ground zircon sand. By adjusting parameters such as the liquid-to-solid ratio and the grinding time, operators can achieve the desired particle size distribution, ensuring consistent quality and uniformity in the final product.
Heat generation during grinding can negatively impact both the grinding media and the material being processed. Wet grinding machines mitigate this issue by dissipating heat through the liquid media, preventing thermal damage to the equipment and the zircon sand. This results in improved product quality, as the material is subjected to minimal thermal stress.

The rapid advancement of technology has revolutionized various industries, and the field of sand processing is no exception. Among the myriad of sand processing techniques, the utilization of zircon sand mill machines has emerged as a game-changer. These cutting-edge machines offer enhanced efficiency, precision, and productivity in the processing of zircon sand, a versatile and valuable material used in numerous applications.
Zircon sand, derived from the mineral zirconium silicate, possesses exceptional properties that make it highly sought after in various industries. It is known for its high melting point, thermal stability, low thermal expansion, and excellent resistance to corrosion and wear. Additionally, zircon sand exhibits remarkable refractory properties, making it an ideal choice for foundry applications. Its versatility extends to sectors such as ceramics, glass manufacturing, electronics, and even nuclear power plants.
Zircon sand mill machines are specialized equipment designed to grind, mill, and process zircon sand particles into fine powders of controlled sizes. These machines utilize advanced milling techniques to break down zircon sand clusters and separate individual grains. The resulting powders can then be used in various downstream applications.
Zircon sand mill machines offer precise control over particle size distribution, allowing manufacturers to tailor the sand powders according to specific requirements. This level of customization ensures optimal performance in diverse applications, from ceramic glazes to investment casting.
By employing high-speed milling and grinding mechanisms, zircon sand mill machines significantly reduce processing time. This acceleration enhances productivity and enables manufacturers to meet growing market demands without compromising on quality.
Zircon sand mill machines provide consistent results by ensuring uniform particle size distribution throughout the sand processing cycle. This uniformity translates into consistent product quality, reducing the risk of defects or variations in the end products.
With zircon sand mill machines, manufacturers can achieve higher yields from raw materials, minimizing wastage and maximizing resource utilization. Additionally, the improved efficiency and productivity of these machines lead to higher throughput, translating into cost savings and competitive advantages.
Our Projects
Copyright © ZENITH, All Right Reserved.