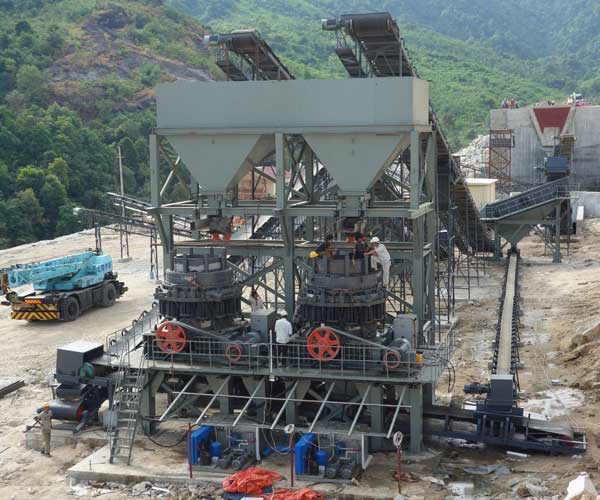
Crushing and grinding are the initial steps in dolomite processing, which involve reducing the size of the raw material to achieve the desired particle size for subsequent applications. Various types of equipment are used for these processes, including jaw crushers, cone crushers, and grinding mills.
24 Online Service

Dolomite powder is a versatile mineral that has a range of applications, from agriculture and construction to cosmetics and pharmaceuticals. The process of transforming dolomite into a fine powder involves crushing, grinding, and sometimes further processing, such as air classification. One critical aspect of dolomite powder that impacts its usability and effectiveness is its mesh size.
Mesh size is a measure used to describe the size of particles in a granular material, like powders. It is a standard unit used to quantify the number of openings per linear inch in a wire mesh screen, which is used to sieve and classify granular materials. For instance, a 100-mesh screen has 100 openings per inch, and a 200-mesh screen has 200 openings per inch. Consequently, the higher the mesh number, the smaller the particle size. When discussing dolomite powder, the mesh size refers to the size of the dolomite particles that can pass through a specific mesh screen.
The mesh size of dolomite powder has a direct impact on its physical and chemical properties, which in turn affects its suitability for different applications. A higher mesh size indicates a finer powder, which can lead to increased reactivity and solubility. On the other hand, a lower mesh size signifies a coarser powder with larger particles, which may have lower reactivity and solubility but improved flowability and lower dust generation. The choice of mesh size for dolomite powder depends on the specific requirements of the intended application.
Dolomite powder is available in a wide range of mesh sizes to cater to various industries and applications. Here are some typical mesh sizes and their associated applications:

Dolomite, a sedimentary rock composed primarily of calcium magnesium carbonate (CaMg(CO3)2), is widely used in various industries, including construction, agriculture, glass manufacturing, and chemical production. Processing dolomite rock effectively is crucial to maximizing its potential and optimizing its applications.
The first step in dolomite processing is to reduce the size of the raw material. This involves crushing and grinding the dolomite rock to achieve the desired particle size, which is crucial for its subsequent applications. Typically, the process begins with primary crushing using jaw crushers, which work by applying compressive force to break the rocks into smaller pieces. Jaw crushers are suitable for handling large feed sizes and can produce a wide range of particle sizes, depending on the crusher’s settings.
Following primary crushing, secondary crushing is often required to further reduce the size of the dolomite rock. Cone crushers are commonly used for this purpose, as they can handle a wide range of particle sizes and provide consistent output. Cone crushers work by applying compressive force to the material between a fixed outer shell and an oscillating inner cone.
After crushing, the dolomite rock is ground to achieve the desired particle size distribution using grinding mills. Various types of grinding mills are available, including ball mills, vertical roller mills, and hammer mills. The choice of grinding mill depends on the required product size, energy efficiency, and operating costs.
Calcination is a critical step in dolomite processing, as it involves heating the crushed and ground material to high temperatures, typically between 900 and 1100°C. This process drives off carbon dioxide (CO2) and water, converting dolomite into calcined dolomite, also known as dolime or dolomitic lime. Calcined dolomite has unique properties, such as improved reactivity and enhanced porosity, making it suitable for a variety of industrial applications.
There are several types of calcination equipment used for dolomite processing, including rotary kilns, shaft kilns, and fluidized bed calciners. Rotary kilns are horizontal, cylindrical furnaces that rotate slowly while the dolomite moves through them. Heat is applied externally, and the rotating motion helps promote uniform heating and calcination. Rotary kilns are widely used due to their versatility, high capacity, and continuous operation.
Shaft kilns, on the other hand, are vertical furnaces that operate in a batch or semi-continuous mode. Dolomite is loaded into the top of the kiln, and heat is applied from the bottom. As the dolomite moves downward, it undergoes calcination and is discharged at the bottom of the kiln. Shaft kilns are energy-efficient and produce a high-quality product but have lower capacity compared to rotary kilns.
Fluidized bed calciners are another type of calcination equipment, which utilizes a bed of hot gas to heat and calcine the dolomite. These calciners offer excellent temperature control, high energy efficiency, and can handle a wide range of feed sizes. However, they may be more complex to operate and maintain compared to rotary and shaft kilns.
After calcination, the dolomite may require further separation and purification to meet the desired specifications for specific applications. Several techniques can be employed for this purpose, including flotation, magnetic separation, and gravity separation.
Flotation is a process in which dolomite particles are separated based on their surface properties. In this technique, a slurry of ground dolomite and water is mixed with various chemicals.
Efficient and effective processing of dolomite is essential for maximizing its potential and optimizing its applications.
Crushing and grinding are the initial steps in dolomite processing, which involve reducing the size of the raw material to achieve the desired particle size for subsequent applications. Various types of equipment are used for these processes, including jaw crushers, cone crushers, and grinding mills.
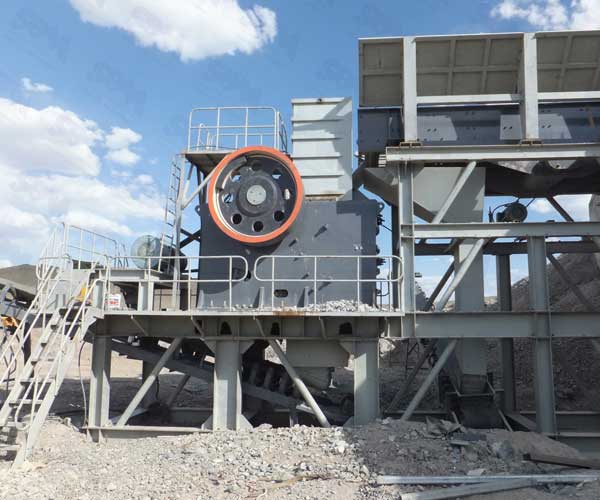

Jaw crushers are commonly used for primary crushing, as they can handle large feed sizes and produce a wide range of particle sizes. They work by applying compressive force to break the rocks into smaller pieces. While jaw crushers are efficient and versatile, they may have limitations in terms of wear and tear, especially when dealing with abrasive materials like dolomite.
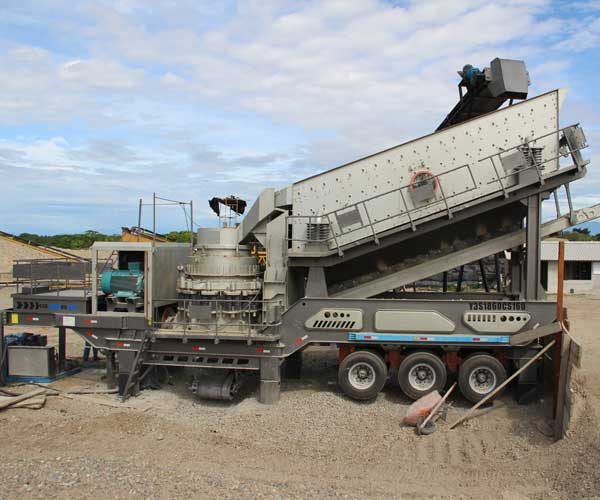

Cone crushers are often used for secondary crushing, providing consistent output with a wide range of particle sizes. They work by applying compressive force to the material between a fixed outer shell and an oscillating inner cone. Cone crushers offer advantages such as higher capacity and lower operating costs compared to jaw crushers, but may require more maintenance.
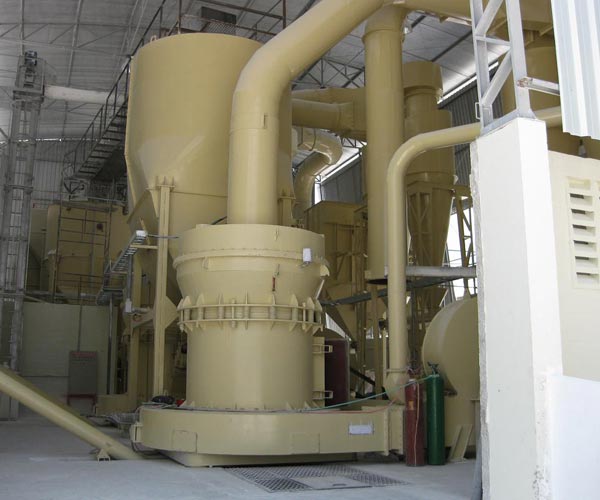

Grinding mills are used to further reduce the particle size of dolomite after crushing. There are several types of grinding mills available, including ball mills, vertical roller mills, and hammer mills. The choice of grinding mill depends on the required product size, energy efficiency, and operating costs.
Calcination is a crucial step in dolomite processing, as it involves heating the crushed and ground material to high temperatures (typically between 900 and 1100°C) to drive off carbon dioxide (CO2) and water, converting dolomite into calcined dolomite or dolime. There are several types of calcination equipment used for dolomite processing, including rotary kilns, shaft kilns, and fluidized bed calciners.
Rotary kilns are horizontal, cylindrical furnaces that slowly rotate while the dolomite moves through them. Heat is applied externally, and the rotating motion promotes uniform heating and calcination. Rotary kilns are widely used due to their versatility, high capacity, and continuous operation.
Shaft kilns are vertical furnaces that operate in a batch or semi-continuous mode. Dolomite is loaded into the top of the kiln, and heat is applied from the bottom. As the dolomite moves downward, it undergoes calcination and is discharged at the bottom of the kiln. Shaft kilns are energy-efficient and produce a high-quality product but have lower capacity compared to rotary kilns.
Fluidized bed calciners utilize a bed of hot gas to heat and calcine the dolomite. These calciners offer excellent temperature control, high energy efficiency, and can handle a wide range of feed sizes. However, they may be more complex to operate and maintain compared to rotary and shaft kilns.
Following calcination, dolomite may require further separation and purification to meet the desired specifications for specific applications. Several techniques can be employed for this purpose, including flotation, magnetic separation, and gravity separation.
Flotation machines are used to separate dolomite particles based on their surface properties. In this process, a slurry of ground dolomite and water is mixed with various chemicals, such as collectors and frothers, which facilitate the separation of dolomite particles from impurities.
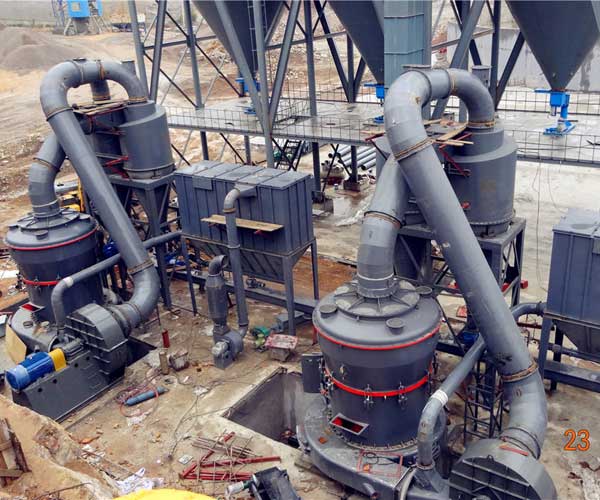

Efficient processing of dolomite is essential for maximizing its potential and optimizing its applications. Selecting the right equipment for dolomite processing is crucial to ensuring an effective and cost-efficient operation.
Understanding the specific characteristics of dolomite is essential for selecting the appropriate processing equipment. Some key factors to consider include:
Defining the processing requirements is critical for selecting the right equipment. Some factors to consider include:
Selecting equipment with high efficiency and reliability is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and minimizing downtime. Factors to consider include:
Ensuring compliance with environmental and safety regulations is essential for any dolomite processing operation. Some factors to consider include:
Balancing capital and operational costs is critical for selecting the most cost-effective dolomite processing equipment. Factors to consider include:

Location:Russia
Material:Granite, dolomite
Input Size:Below 425mm
Output Size:0-5-10-15-40mm
Capacity:50t/h
Application: Supplied to asphalt mixing plants
Equipment:KE500F110-4 Portable Crushing Plant (four-combination type)XSD2610 Sand Washer
Our Projects
Copyright © ZENITH, All Right Reserved.