Coal is primarily used as a fuel source for electricity generation and industrial processes. It is burned in power plants to produce steam, which drives turbines to generate electricity. Coal can also be used as a source of heat in homes and businesses, as well as in the production of steel, cement, and other industrial products.
24 Online Service

Coal is typically extracted through underground mining or surface mining methods, and it comes in various grades, ranging from lignite (the lowest grade) to anthracite (the highest grade). The quality and composition of coal depend on factors such as the type of plant material that formed it, the temperature and pressure during its formation, and the length of time it was buried.
Coal is primarily used as a fuel source for electricity generation and industrial processes. However, the burning of coal also produces pollutants such as carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, and nitrogen oxide, which contribute to air pollution and climate change. As a result, there is growing interest in transitioning to cleaner and more sustainable sources of energy.
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock that is primarily composed of carbon, along with various other elements such as sulfur, nitrogen, and oxygen. Coal has been used as a source of energy for centuries, and it remains a major source of energy worldwide today. However, the use of coal has been a controversial topic due to its negative impact on the environment and human health.
One of the primary uses of coal is to produce electricity. Coal-fired power plants generate about 38% of the electricity produced in the United States. The process of generating electricity from coal involves burning the coal to heat water, which produces steam. The steam then drives turbines that generate electricity. Although coal-fired power plants are relatively inexpensive to build and operate, they emit large amounts of carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and other pollutants that contribute to climate change and air pollution.
Another use of coal is to produce steel. Coal is used as a fuel in the production of coke, which is a key ingredient in the steel-making process. Coke is made by heating coal in the absence of air to drive off volatile compounds and leave behind carbon-rich material. This carbon-rich material is then mixed with iron ore and other materials in a blast furnace to produce molten iron. The molten iron is then processed to produce steel. However, the production of coke also produces large amounts of carbon dioxide and other pollutants.
Coal is also used as a fuel for heating homes and buildings. In many parts of the world, coal is still used as the primary source of heat in homes and buildings. However, burning coal for heating produces large amounts of carbon dioxide and other pollutants, and it can also contribute to indoor air pollution and health problems.
In addition to its use as a source of energy and fuel, coal is also used in a variety of other applications. For example, coal is used in the production of chemicals such as methanol and synthetic fibers. Coal is also used as a feedstock for the production of activated carbon, which is used in a variety of applications such as water filtration, air purification, and medical treatments.
In its natural state, coal is a solid rock-like substance that needs to be mined and processed to extract its energy content. One important step in this process is crushing coal into smaller pieces.

Coal crushing refers to the process of breaking down large chunks of coal into smaller pieces, which can then be used for various purposes such as power generation, industrial production, and heating. Coal crushing is a crucial step in the coal mining process as it enables the extraction of coal from the earth and makes it suitable for use in various applications.
The process of coal crushing involves several stages, each of which is essential in breaking down the coal into the desired size and quality. The first stage of coal crushing is the primary crushing stage, which involves the use of a crusher to break down the larger pieces of coal into smaller, more manageable sizes. Typically, crushers used in coal crushing are jaw crushers, impact crushers, and cone crushers.
Once the coal has been crushed to the desired size, it is then sorted and processed further. The next stage of coal processing is screening, where the coal is separated into different sizes based on its particle size distribution. This is important as different sizes of coal are used for different purposes. For example, larger pieces of coal are typically used in power generation, while smaller pieces of coal are used in industrial production.
After screening, the coal is typically washed to remove impurities and improve its quality. Coal washing involves the use of water and chemicals to separate the coal from impurities such as sulfur, ash, and rock. This process can improve the quality of the coal and make it more suitable for use in various applications.
In addition to crushing, screening, and washing, coal may also undergo further processing to make it suitable for specific applications. For example, coal may be pulverized into a fine powder and used as a fuel in power plants. This process is known as pulverization, and it involves grinding the coal to a fine powder and then injecting it into a boiler to produce steam.

Coal powder, also known as pulverized coal, is a fine-grained coal that has been ground to a powder form. It is typically used as a fuel in power plants and other industrial applications where high temperatures are required for energy production.
The process of pulverizing coal involves crushing the coal into small particles and then blowing it into a furnace, where it is burned to generate heat. This process is known as combustion, and it releases energy in the form of heat that can be used to generate steam and drive turbines.
Coal powder has several advantages over traditional solid coal fuel. It is easier to transport and store, and it burns more efficiently, producing fewer emissions of pollutants such as sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides. However, the process of producing coal powder can be expensive, and it requires a significant amount of energy to grind the coal into a fine powder.
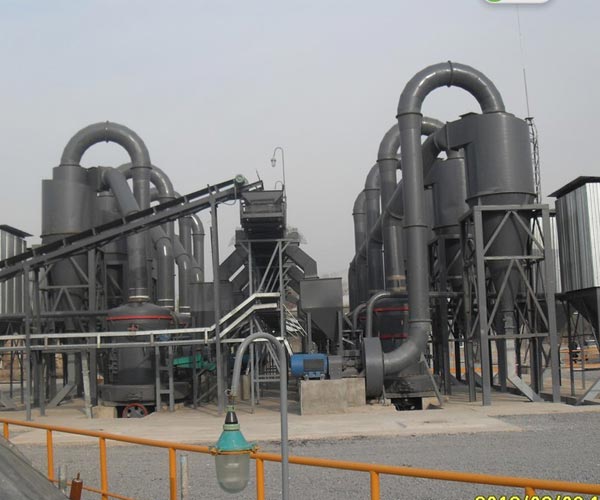
Coal grinding is a crucial process in the power generation industry. It is the process of breaking down coal into smaller pieces to increase its surface area and make it more reactive. The resulting coal dust is used as fuel in power plants, where it is burned to produce electricity. Coal grinding is a complex process that requires specialized equipment and expertise to ensure efficient and safe operation.
Coal grinding involves the use of mechanical equipment to crush and grind coal into powder form. The process begins by feeding the coal into a mill, where it is pulverized into a fine powder. The coal powder is then blown into a combustion chamber of a boiler, where it is burned to produce steam. The steam is then used to drive a turbine, which in turn drives a generator to produce electricity.
There are several types of coal mills used in power plants, including ball mills, bowl mills, roller mills, and hammer mills. Each type of mill operates differently, and each has its advantages and disadvantages. Ball mills are the most common type of coal mill, and they are used to grind coal into a fine powder. Bowl mills are similar to ball mills but have a larger diameter and are used to crush coal into smaller pieces. Roller mills use rollers to crush and grind coal, while hammer mills use hammers to crush and grind coal.
Coal grinding is a critical process in power generation because it affects the efficiency and safety of power plants. Improper coal grinding can result in a loss of power generation capacity, increased maintenance costs, and safety hazards. For example, if coal is not ground finely enough, it will not burn efficiently, leading to a reduction in power generation capacity. On the other hand, if coal is ground too finely, it can form combustible dust that can ignite and cause explosions.
To ensure efficient and safe coal grinding, power plants use specialized equipment and follow strict safety procedures. The equipment used for coal grinding includes mills, crushers, and classifiers. These machines are designed to operate under high pressure and temperature conditions and are made from materials that can withstand wear and tear. The equipment is also equipped with safety features such as explosion-proofing and fire suppression systems.
Coal grinding mills are machines that are used to grind coal into fine particles for efficient combustion in industrial boilers and furnaces. Coal grinding is an essential process in power plants, cement plants, and other industries where coal is used as a fuel. There are different types of coal grinding mills available in the market, each with its unique characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages. In this article, we will discuss the different types of coal grinding mills.
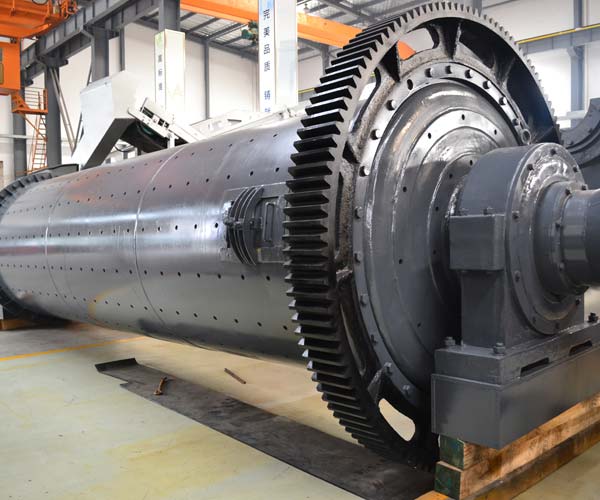

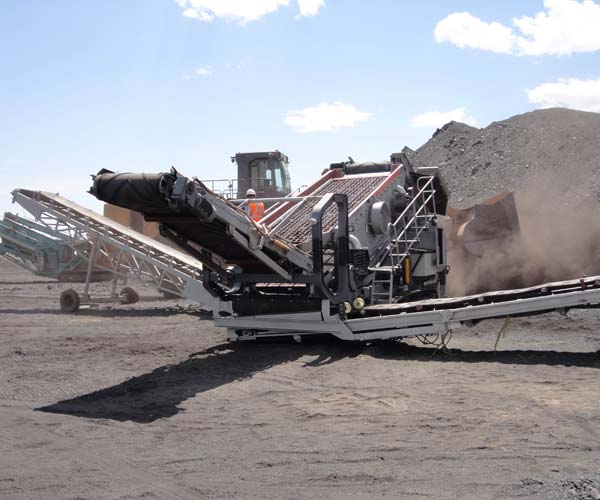
Ball mills are the most common type of coal grinding mills used in power plants. They consist of a rotating drum filled with steel balls that crush the coal into a fine powder. The ball mill rotates at a speed of 70-80% of the critical speed, and the coal is ground by the impact of the steel balls as they fall and strike the coal. The efficiency of ball mills depends on several factors, including the size of the grinding media, the speed of rotation, and the size of the feed material.
The main advantage of ball mills is their versatility. They can be used for grinding a wide range of materials, including coal, limestone, and ores. However, they are not very efficient when it comes to grinding hard coals, and they consume a lot of energy.

Vertical roller mills (VRMs) are becoming increasingly popular in the coal grinding industry. They consist of a large vertical roller that rotates around its axis and a stationary grinding table. The coal is fed into the center of the table, and the rollers crush the coal into fine particles.
VRMs offer several advantages over ball mills. They are more energy-efficient and have a lower specific power consumption. They are also more flexible in terms of the type of coal they can grind and can handle a wider range of materials, including biomass and waste materials.

Roller mills are another type of coal grinding mill commonly used in power plants. They consist of a rotating roll that contains a grinding ring and several rollers. The coal is fed into the bowl through a central inlet, and the rollers crush the coal against the grinding ring. The ground coal is then discharged from the roll through an outlet.
Roller mills are efficient in grinding hard coals and are used in power plants where high-quality coal is available. However, they are not very flexible and cannot grind other materials, such as biomass.

Hammer mills are used for grinding soft and medium-hard materials, including coal. They consist of a series of hammers that rotate at high speed and impact the material being ground. The size of the grinding chamber and the number of hammers can vary, depending on the application.
Hammer mills are suitable for grinding coal with a low moisture content and are commonly used in small-scale coal grinding applications. However, they are not very efficient and are not suitable for grinding hard coals.
Our Projects
Copyright © ZENITH, All Right Reserved.