While portable crushers may offer lower initial purchase prices and simplicity in maintenance, they can incur higher fuel and transportation costs, as well as faster depreciation. Stationary crushers, on the other hand, come with a higher upfront cost but may prove more cost-effective in the long term, thanks to lower maintenance, reduced fuel expenses, and better resale value.
24 Online Service

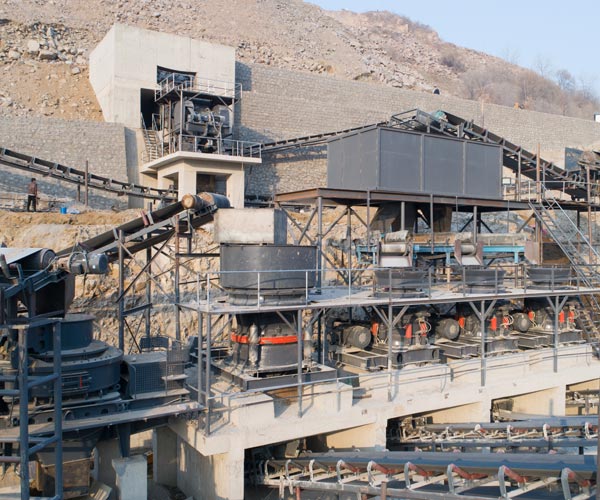
In the world of construction, mining, and recycling, the need to efficiently crush and process materials on-site is paramount. Traditional stationary crushers have long been the go-to solution, but with advancements in technology, portable crusher machines have emerged as a game-changer. These mobile marvels offer a range of benefits, from enhanced mobility to versatility, and have transformed industries in profound ways.
Portable crusher machines, often referred to as mobile crushers or mobile crushing plants, are compact and mobile units designed to crush a variety of materials directly at the job site. Unlike their stationary counterparts, these crushers are mounted on wheels or tracks, making them easily transportable from one location to another. They come in various sizes and configurations to suit different crushing needs, from small-scale construction projects to large-scale mining operations.
The fundamental principle behind portable crusher machines is to break down large chunks of material into smaller, more manageable pieces. This process is achieved through the use of mechanical force, typically involving a combination of crushing mechanisms such as jaw crushers, impact crushers, cone crushers, or even a combination of these.
Jaw Crushers: These crushers use a fixed jaw and a moving jaw to create compression and crush the material. The material is fed into the crusher’s chamber, and the jaws exert pressure to reduce it to the desired size.
Impact Crushers: Impact crushers utilize high-speed rotor impacts to crush materials. Material is fed into the crusher’s chamber and is struck by rapidly spinning hammers or blow bars, breaking it into smaller pieces.
Cone Crushers: Cone crushers operate by compressing material between an eccentrically rotating mantle and a concave bowl liner. This action results in the material being crushed or broken down into finer particles.
The portable nature of these machines allows them to be transported to the site where materials need to be processed, reducing the need for expensive transportation of raw materials to a central processing facility. This not only saves time but also significantly cuts down on transportation costs.
The most apparent advantage of portable crushers is their mobility. They can be easily moved from one location to another, providing the flexibility to crush materials at various job sites. This is particularly beneficial in industries where the source of raw materials is scattered or when crushing is required at multiple locations.
Portable crushers can lead to substantial cost savings in several ways. First, as mentioned earlier, they eliminate the need for extensive material transportation. Second, they reduce the need for additional equipment and manpower since the crushing process can be integrated into the same site where materials are sourced or excavated.
The reduced need for material transportation also contributes to a smaller carbon footprint, as it reduces emissions associated with hauling heavy materials over long distances. Additionally, modern portable crushers are designed with environmental considerations in mind, such as incorporating dust suppression systems to minimize airborne particles.
Portable crushers can improve operational efficiency by allowing materials to be processed immediately after extraction. This reduces the waiting time and streamlines operations, leading to higher productivity and shorter project timelines.
These machines can handle a wide range of materials, from concrete and asphalt to rock, gravel, and even demolition waste. Their adaptability makes them invaluable in diverse industries, including construction, mining, and recycling.
To illustrate the real-world impact of portable crusher machines, let’s explore a few case studies across different industries.
In urban construction projects, the need to recycle and reuse materials is growing in importance. Portable crushers have been instrumental in crushing and recycling concrete and asphalt on-site, reducing the demand for new aggregates and minimizing waste. For instance, in a recent renovation project in New York City, portable crushers were used to process demolished concrete, allowing the construction company to reuse the crushed material as a base for the new construction, saving both money and resources.
In remote mining operations, the ability to bring crushers to the mining site is a game-changer. Portable crushers enable miners to crush ore at the excavation site, eliminating the need for costly transportation to processing plants. For instance, a gold mining company operating in a remote part of Alaska increased its production efficiency by utilizing portable crushers on-site, resulting in substantial cost savings and increased profitability.
The recycling of materials like asphalt and concrete has become a priority in many regions. Portable crushers are indispensable in recycling facilities, where they can process construction and demolition waste into reusable aggregates. A recycling plant in Europe reported a significant increase in its capacity and throughput after incorporating portable crushers into their operations, reducing the need for landfill disposal and promoting sustainability.

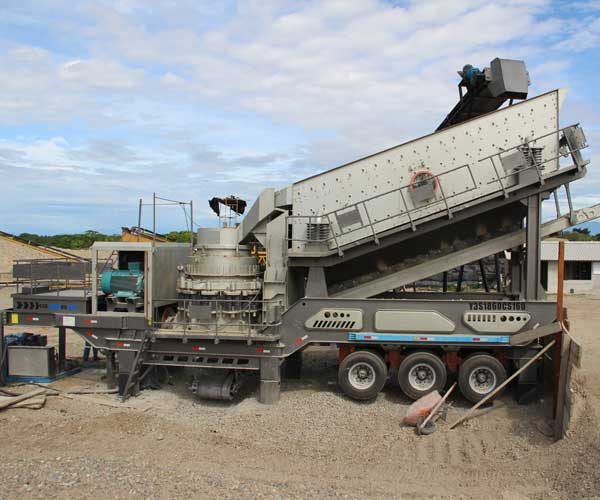
In the world of heavy machinery and construction, innovation has always been the driving force behind enhanced efficiency and productivity. One such innovation that has transformed the way we process and recycle materials is the stationary crusher machine. These formidable machines have revolutionized the construction and mining industries, offering unmatched capacity and stability.
Stationary crusher machines, as the name suggests, are heavy-duty crushing machines that remain fixed in one place, as opposed to their mobile counterparts, which can be transported to various work sites. These machines are primarily designed for industries that require consistent and high-capacity crushing of materials. Stationary crushers come in various types, including jaw crushers, cone crushers, impact crushers, and gyratory crushers, each tailored to specific applications.
Mining: Stationary crushers play a pivotal role in mining operations by breaking down large rocks and ores into smaller, manageable pieces. This facilitates easier handling and processing further downstream.
Construction: In the construction industry, stationary crushers are used to crush concrete, asphalt, and other construction materials, providing the necessary aggregates for building projects.
Quarrying: Quarries rely heavily on stationary crushers to crush and sort various types of rock and stone, which are then used in road construction, concrete production, and landscaping.
Recycling: Stationary crushers are instrumental in recycling operations, where they can crush and process recycled materials like concrete, asphalt, and bricks for reuse in new construction projects.
Higher Capacity: Perhaps the most significant advantage of stationary crushers is their remarkable capacity. These machines are built to handle massive amounts of material continuously, making them ideal for large-scale industrial operations.
Stability and Durability: Stationary crushers are built to last. Their robust construction ensures they can withstand the harshest working conditions, providing a stable and reliable crushing solution.
Consistency: Unlike mobile crushers that may need to be relocated frequently, stationary crushers offer consistent and uninterrupted crushing, minimizing downtime and maximizing productivity.
Precise Control: Stationary crushers are equipped with advanced control systems that allow operators to fine-tune the crushing process, ensuring the desired product size and quality.
Reduced Transportation Costs: By eliminating the need to move the crusher from site to site, stationary crushers reduce transportation costs, fuel consumption, and emissions.
The Limestone Quarry Example: A limestone quarry in the heart of the United States faced the challenge of meeting increasing demand for high-quality aggregates. They invested in a stationary jaw crusher that could handle large volumes of rock. This decision led to a substantial increase in production capacity, and the quarry was able to supply the required materials consistently, resulting in increased profitability.
In a recycling center in Europe, stationary crushers were employed to process and recycle concrete and asphalt waste from construction and demolition sites. The crushers efficiently turned this waste into valuable recycled materials, reducing the need for new raw materials and contributing to a more sustainable construction industry.
A large copper mining operation in South America turned to stationary cone crushers to crush the copper ore efficiently. The reliability and high capacity of the stationary crushers ensured that the operation met its production targets consistently, even in challenging geological conditions.
On a major construction project in Asia, stationary crushers were used to process and crush materials directly on-site, reducing the need for transportation and minimizing the environmental impact. This approach saved both time and money while maintaining the desired product quality.

In the world of aggregate production, the choice between portable and stationary crushers is a critical decision that directly impacts a company’s bottom line. While both options serve the primary purpose of crushing rocks and minerals into various sizes, the costs associated with each type of crusher can vary significantly.
The initial purchase price is the most apparent and often the first consideration when choosing between portable and stationary crushers. Generally, portable crushers tend to have a lower upfront cost compared to stationary crushers. This is because portable crushers are designed to be mobile, allowing them to be moved from site to site, which often results in a simpler and less costly installation process.
However, the initial purchase price should not be the sole factor driving the decision-making process. Stationary crushers, while more expensive upfront, can offer advantages in terms of capacity and efficiency. It’s essential to analyze the specific needs of the operation and evaluate whether the higher upfront investment is justified by long-term benefits.
Maintenance costs play a crucial role in the overall cost analysis of crushers. Portable crushers are known for their simplicity, which can translate into lower maintenance costs. They have fewer components and typically require less frequent maintenance. On the other hand, stationary crushers, with their complex machinery and greater throughput capacity, may incur higher maintenance expenses.
To illustrate this point, let’s consider an example. A portable jaw crusher might have lower maintenance costs due to its simplicity and lower throughput, while a stationary cone crusher, with its more intricate design and higher capacity, could incur higher maintenance costs. Companies need to assess their operational needs and maintenance budgets when deciding between the two options.
Fuel costs are a significant consideration, particularly for portable crushers that require mobility. Portable crushers are powered by diesel engines, and fuel expenses can accumulate quickly, especially when transporting the equipment between different job sites. In contrast, stationary crushers are usually connected to the electrical grid, reducing their reliance on expensive diesel fuel.
It’s worth noting that advancements in technology have led to more fuel-efficient engines for portable crushers, but fuel expenses should still be carefully considered when conducting a cost analysis.
Transportation costs are inherent to portable crushers since they need to be moved between various work sites. The distance between job locations, the size of the equipment, and the fuel efficiency of the transportation method all influence transportation costs. These costs can be significant, especially if the crusher needs to be relocated frequently.
On the other hand, stationary crushers are set up at a fixed location, eliminating the need for transportation between sites. This can lead to cost savings in terms of time, fuel, and logistical planning.
When comparing the costs of portable and stationary crushers, it’s essential to consider their respective lifespans and depreciation rates. Portable crushers often have a shorter lifespan due to the wear and tear associated with frequent movement and setup. Consequently, they may depreciate more rapidly than stationary crushers.
Stationary crushers, being permanently installed, tend to have a longer lifespan and slower depreciation rate. This can result in better long-term cost efficiency, as they may require replacement or major refurbishments less frequently than their portable counterparts.
Resale value is another factor that should not be overlooked in the cost analysis. Stationary crushers often retain a higher resale value compared to portable crushers. This is because stationary crushers are typically well-maintained and have lower wear and tear due to their fixed location and lower mobility. In contrast, portable crushers may have reduced resale value due to their higher likelihood of wear and damage from transportation.
To further illustrate this point, consider the scenario where a company decides to upgrade its crushing equipment. A stationary crusher could fetch a higher resale value, potentially offsetting some of the initial investment costs. In contrast, a portable crusher may have a lower resale value, impacting the overall cost equation.
To provide a clear cost comparison between portable and stationary crushers, we will use a hypothetical case study. Let’s assume a company is in the business of aggregate production and needs to choose between a portable jaw crusher and a stationary cone crusher. We will break down the costs over a 10-year period, including initial purchase, maintenance, fuel, and transportation costs, while factoring in the equipment’s lifespan and potential resale value.
| Cost Element | Portable Jaw Crusher ($) | Stationary Cone Crusher ($) |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Purchase Price | 500,000 | 1,200,000 |
| Maintenance Costs | 100,000 | 150,000 |
| Fuel Costs (10 years) | 250,000 | – |
| Transportation Costs | 300,000 | – |
| Depreciation (10 years) | 200,000 | 100,000 |
| Resale Value (est.) | 200,000 | 600,000 |
| Total Cost (10 years) | 950,000 | 650,000 |
In this example, the portable jaw crusher has a lower initial purchase price, but it incurs higher maintenance, fuel, and transportation costs over a 10-year period. Additionally, due to its higher depreciation rate and lower estimated resale value, the portable crusher ends up costing more than the stationary cone crusher in the long run.
Our Projects
Copyright © ZENITH, All Right Reserved.