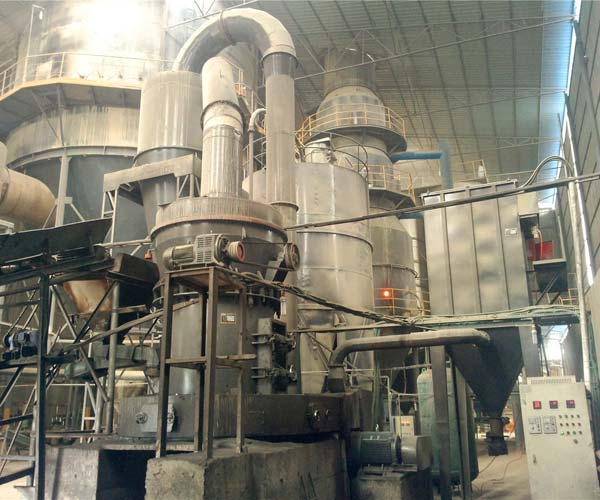
A coal pulverizer mill is a complex machine consisting of several key components, each with a specific function and importance in the energy generation process. Understanding these components and their roles is crucial for maintaining the efficiency, reliability, and environmental performance of coal-fired power plants.
24 Online Service
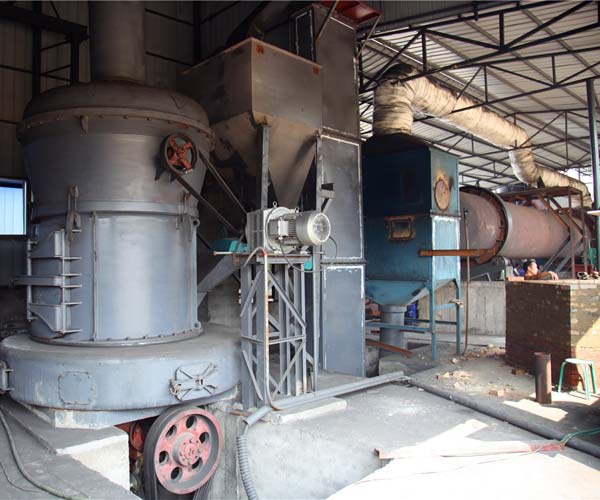

Coal pulverization is the process of reducing coal into a fine powder or dust in order to improve its combustion efficiency in various energy generation systems. The goal of coal pulverization is to increase the surface area of coal particles and ensure a consistent particle size distribution. This, in turn, facilitates efficient and complete combustion, resulting in higher energy output and reduced emissions.
Coal pulverization is of paramount importance in energy production for several reasons:
By pulverizing coal into fine particles, its surface area increases significantly. This increased surface area allows for better mixing with air, enhancing the combustion process. As a result, the overall combustion efficiency of coal is improved, leading to greater energy production.
Coal pulverization ensures a consistent particle size distribution, which leads to uniform burn rates during combustion. This uniformity prevents hotspots and incomplete combustion, reducing the emission of harmful pollutants such as carbon monoxide and particulate matter.
The efficient combustion of pulverized coal results in higher energy output per unit of coal consumed. This increased energy yield is crucial for meeting the growing energy demands of modern society.
Improved combustion efficiency also translates into lower emissions of greenhouse gases and air pollutants, contributing to a cleaner and more sustainable energy production process.
Coal pulverizer mills are specialized machinery designed to crush and grind coal into the fine powder required for efficient combustion. These mills are an integral part of coal-fired power plants, industrial boilers, and other energy generation systems. They come in various designs and configurations, but their primary purpose remains the same: to pulverize coal effectively.
Here’s how coal pulverizer mills play a crucial role in the coal pulverization process:
Different types of coal are used in pulverization, and their characteristics can significantly impact the pulverization process and its efficiency. The key types of coal used include:
Anthracite is a high-rank coal known for its high carbon content and low moisture and volatile matter content. It is relatively easy to pulverize and is preferred in applications where high combustion efficiency is essential. Anthracite coal produces relatively low emissions when burned.
Bituminous coal is the most common type used in pulverization. It contains a moderate amount of carbon, along with some moisture and volatile matter. Bituminous coal is versatile and can be efficiently pulverized for use in various combustion systems.
Sub-bituminous coal contains a higher moisture and volatile matter content compared to bituminous coal. While it can be pulverized, its higher moisture levels may require additional drying before combustion. Sub-bituminous coal is commonly used in power plants due to its abundance.
Lignite, often referred to as brown coal, has the highest moisture content and the lowest carbon content among coal types. Pulverizing lignite can be challenging due to its high moisture levels, but it is used in regions where it is abundant. However, lignite combustion may produce higher emissions.
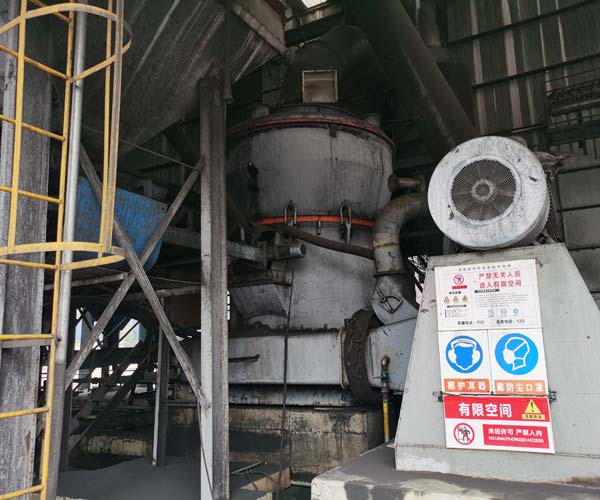

One essential element in this process is the coal pulverizer mill. This engineering marvel plays a pivotal role in transforming raw coal into fine, efficient fuel for combustion in power plants. To understand the significance of this machine, it’s crucial to dissect its key components and grasp their functions.
At the core of a coal pulverizer mill are the grinding rollers and table. These components work together to crush and grind the raw coal into a fine powder. The grinding table is a flat, rotating surface where the coal is fed and ground. It is usually made of cast steel or other wear-resistant materials to withstand the abrasive nature of coal.
The grinding rollers, typically placed above the grinding table, exert immense pressure on the coal as it passes between them and the table. They are mounted on a rotating shaft and are designed to crush the coal into smaller particles. The precise design of the grinding rollers and table is critical to achieving the desired coal fineness, which directly impacts combustion efficiency and emissions.
Grinding Efficiency: The grinding rollers and table are responsible for reducing the coal to the desired size. Efficient grinding ensures that the coal particles are finely ground, facilitating better combustion and heat generation.
Particle Size Control: The coal fineness achieved by these components directly influences the combustion process’s stability and efficiency. Controlling the particle size distribution is crucial to optimize power plant performance.
Air heaters and classifiers are essential components that aid in the coal pulverizing process. They work together to maintain the desired coal temperature and separate the fine coal particles from the coarse ones.
Air heaters, as the name suggests, are responsible for heating the incoming air used in the combustion process. They help in achieving the optimal temperature for efficient coal combustion. These heaters use heat recovered from the hot flue gases to preheat the incoming air, enhancing the overall energy efficiency of the system.
Classifiers are used to separate fine coal particles from larger ones. They ensure that only the properly sized coal particles are delivered to the combustion chamber, improving combustion efficiency and reducing emissions. Classifiers achieve this separation by utilizing centrifugal forces or other classification methods.
Temperature Control: Air heaters maintain the proper temperature of the incoming air, ensuring that the coal burns efficiently and minimizing the risk of slagging and fouling in the furnace.
Particle Separation: Classifiers ensure that only appropriately sized coal particles enter the combustion chamber. This helps in preventing large, unburned coal particles from being carried over into the flue gas, which can lead to increased emissions.
Primary air fans play a critical role in supplying the necessary air for combustion. These fans are responsible for delivering a controlled amount of air to the pulverizer mill and the combustion chamber.
Oxygen Supply: Primary air fans provide the primary source of oxygen for the combustion process. Proper control of primary air ensures that the coal is burned efficiently and that combustion by-products are within acceptable limits.
Seal air fans are specialized fans that serve a critical purpose in maintaining the integrity of the pulverizer mill. They create a barrier of air between the pulverizer and the atmosphere, preventing the ingress of contaminants.
Contamination Prevention: Seal air fans ensure that foreign particles, such as dust and moisture, do not enter the pulverizer mill, which could lead to equipment damage or reduced performance.
Pulverized coal burners are the endpoints of the coal pulverization process, where the finely ground coal is injected into the combustion chamber of the boiler. These burners are designed to efficiently mix the pulverized coal with air for complete combustion.
Efficient Combustion: Pulverized coal burners ensure that the coal is evenly distributed and mixed with air to facilitate efficient and clean combustion, maximizing energy generation while minimizing emissions.
Coal feeders are responsible for delivering a consistent and controlled supply of raw coal to the pulverizer mill. They ensure that the mill operates at a constant feed rate, which is essential for stable and efficient combustion.
Feed Rate Control: Coal feeders maintain a uniform flow of coal into the pulverizer, preventing overloading or underfeeding, which can result in unstable combustion and reduced power generation.
Drive mechanisms are the mechanical systems responsible for powering the various components of the coal pulverizer mill. These mechanisms include motors, gears, and other transmission elements that enable the precise control of the mill’s operations.
Component Operation: Drive mechanisms ensure that all components of the pulverizer mill, such as the grinding rollers, table, and classifiers, operate smoothly and in coordination, contributing to the overall efficiency and reliability of the system.
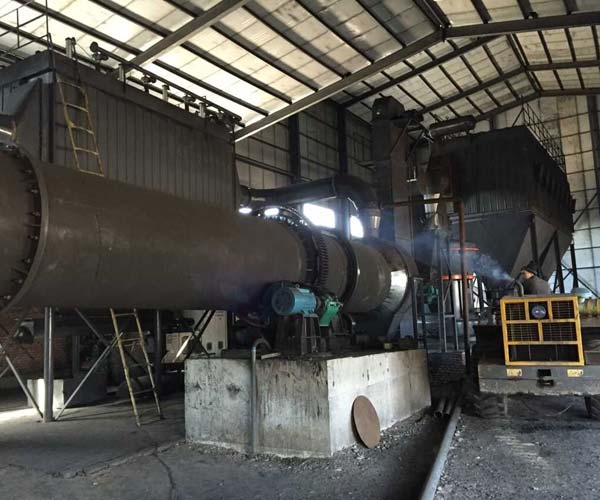

In the ever-evolving landscape of energy production, coal remains a significant player, despite the growing emphasis on cleaner and more sustainable alternatives. To harness the energy stored within coal efficiently, power plants rely on coal pulverizer mills. These complex machines are vital in reducing coal to a fine powder, facilitating combustion and heat generation.
The journey of coal within a pulverizer mill begins with coal feeding and drying. Coal, usually in the form of chunks or chunks of coal, is fed into the mill through a central inlet pipe. This raw coal must undergo drying to eliminate any moisture content before it can be effectively pulverized. Moisture in coal can hinder the combustion process, leading to reduced efficiency and increased emissions.
In this phase, the coal is exposed to hot air within the mill. The hot air serves a dual purpose: it dries the coal and carries it towards the grinding and pulverization section. Maintaining the correct temperature and airflow is essential in ensuring that the coal is adequately dried without being overheated, which could potentially lead to combustion within the mill itself.
Once the coal is sufficiently dried, it moves into the grinding and pulverization phase, where the magic happens. The coal is ground down into a fine powder through a combination of mechanical forces and impact. This fine powder is essential for efficient combustion, as it increases the surface area of the coal particles exposed to oxygen during the combustion process.
The critical parameters to monitor and control during this phase include the grinding roll pressure, grinding roll speed, and the clearance between the grinding roll and the grinding ring. These parameters determine the fineness of the coal powder produced, and fine-tuning them ensures optimal combustion efficiency and minimizes wear and tear on the mill components.
After the coal is pulverized into a fine powder, it enters the classification and separation stage. Here, the powdered coal is separated from larger particles, ensuring that only the finest particles are carried forward for combustion. This separation is achieved through a combination of centrifugal force and airflow.
Operators must carefully monitor and control the airflow rates and classifier settings during this phase. Adjusting these parameters allows for precise control over the particle size distribution of the coal powder, which is crucial for achieving efficient combustion and reducing emissions. Oversized particles can lead to incomplete combustion, while undersized particles can result in excessive heat generation and damage to the combustion equipment.
The heart of the coal pulverizer mill’s operation lies in the combustion and heat generation process. The finely pulverized coal is injected into the furnace of a power plant boiler, where it is mixed with preheated air and ignited. This combustion process releases the energy stored in coal in the form of heat, which is then used to produce steam to drive turbines and generate electricity.
During combustion, operators must closely monitor critical parameters such as air-fuel ratio, furnace temperature, and the performance of combustion controls. Maintaining the right balance of air and fuel is essential for achieving efficient combustion. Deviations from the optimal air-fuel ratio can lead to reduced efficiency and increased emissions. Additionally, monitoring and controlling furnace temperature ensure that the combustion process occurs at the desired level of intensity.
Efficient operation of a coal pulverizer mill hinges on the precise monitoring and control of several critical parameters throughout the process:
Our Projects
Copyright © ZENITH, All Right Reserved.